Figure 1.
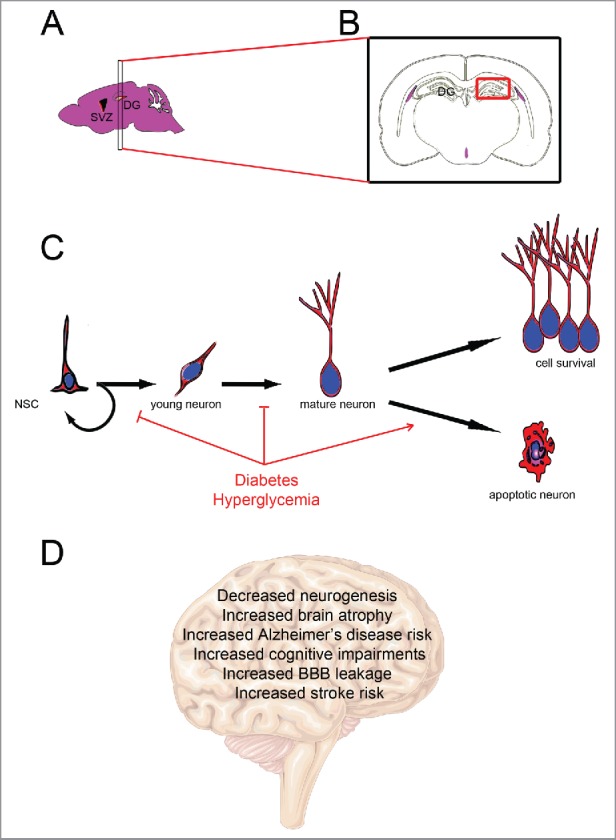
Diabetes impairs adult neurogenesis and brain functions. (A) Sagittal mouse brain section showing the main neurogenic regions: the subventricular zone of the lateral ventricle (SVZ) and the subgranular region of the dentate gyrus of the hippocampus (DG). (B) Coronal section through the dentate gyrus of the hippocampus corresponding to the most studied neurogenic region in diabetes. (C) Neurogenic processes involve neural stem cell proliferation (including self-renewing) and the generation of young neurons that differentiate into mature neurons and integrate preexisting neural networks. Diabetes/hyperglycemia has been shown to inhibit neural stem cell proliferation and neuronal differentiation, and to promote apoptosis. (D) Effects of diabetes on brain functions and physiology.
