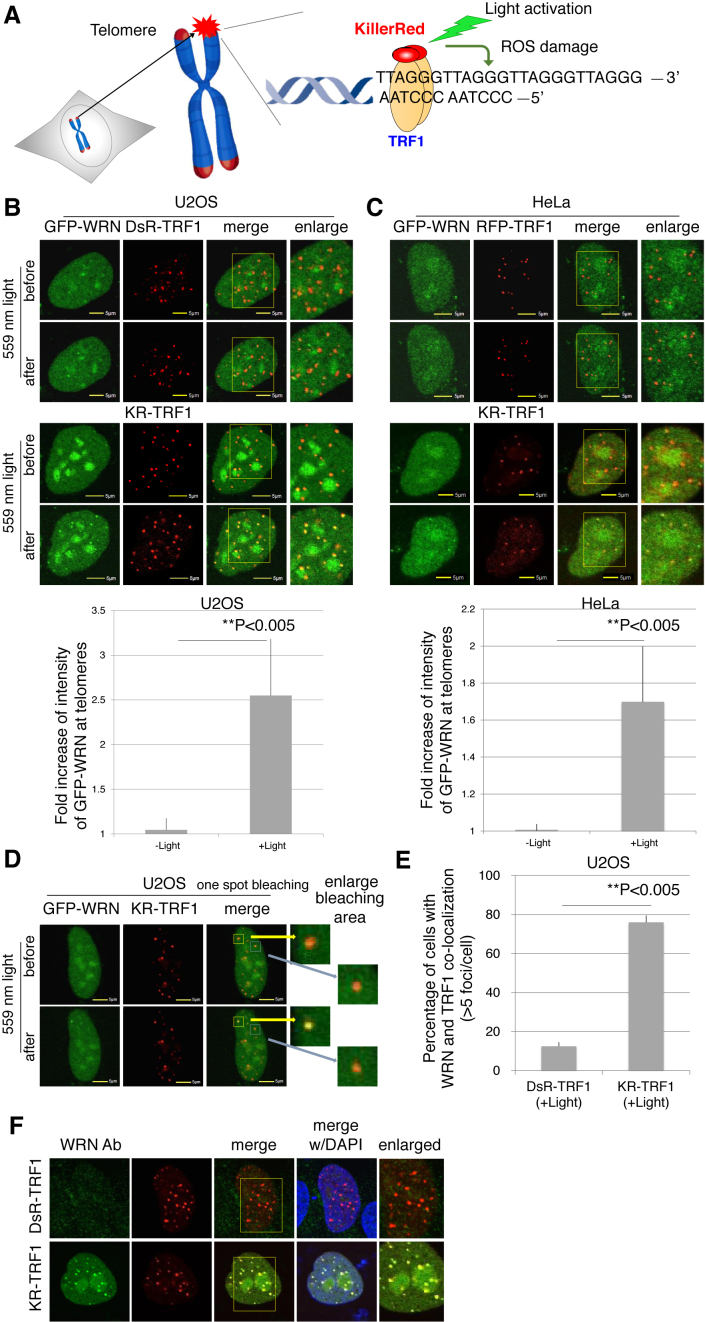
Figure 1.
WRN is recruited to sites of oxidative DNA damage at telomeres. (A) Overview of the Damage Targeted at Telomeres method to induce ROS damage specifically at sites of telomeres. KillerRed (KR) is fused with TRF1 to bind to telomeric DNA repeats. Exposure of cells to visible light will activate KR to induce oxidative DNA damage at telomeres in living cells. (B and C) GFP-WRN and KR-TRF1, or DsR-TRF1 or RFP-TRF1, were co-transfected into U2OS cells (B) and HeLa cells (C). The single cell nucleus was scanned by a 559 nm laser; recruitment of WRN to KR-TRF1 damage sites in both U2OS (B) and HeLa cells (C) 3 min after activation is shown (upper panel). Quantification of the damage response of GFP-WRN at sites of KR-TRF1 (lower panel). The fold increase of GFP-WRN (mean intensity of WRN at KR-TRF1/mean intensity of GFP-WRN distant from KR-TRF1 in the nucleus) is shown in the U2OS cell line (B) and HeLa cell line (C). Data are represented as mean ± SEM, **P < 0.005. (D) GFP-WRN and KR-TRF1 were co-transfected into U2OS cells and one KR-TRF1 spot (indicated by a yellow square) was scanned by the 559 nm laser to activate KR; recruitment of WRN to the single KR-TRF1 spot is shown 3 min after activation. GFP-WRN at an inactivated KR-TRF1 spot is shown in the blue square. (E and F) Damage response of endogenous WRN at sites of telomeres is shown. U2OS cells synchronized at G0/G1 phase expressing either DsR-TRF1 or KR-TRF1 were exposed to a 15 W SYLVANIA cool white fluorescent bulb for 20 min and then immunostained with WRN antibody. Percentage of colocalization of WRN and DsR-TRF1 or KR-TRF1 (>5 colocalization spots were defined as positive) is shown. A total of 150 cells in total were counted in three independent experiments, data are represented as mean ± SEM.