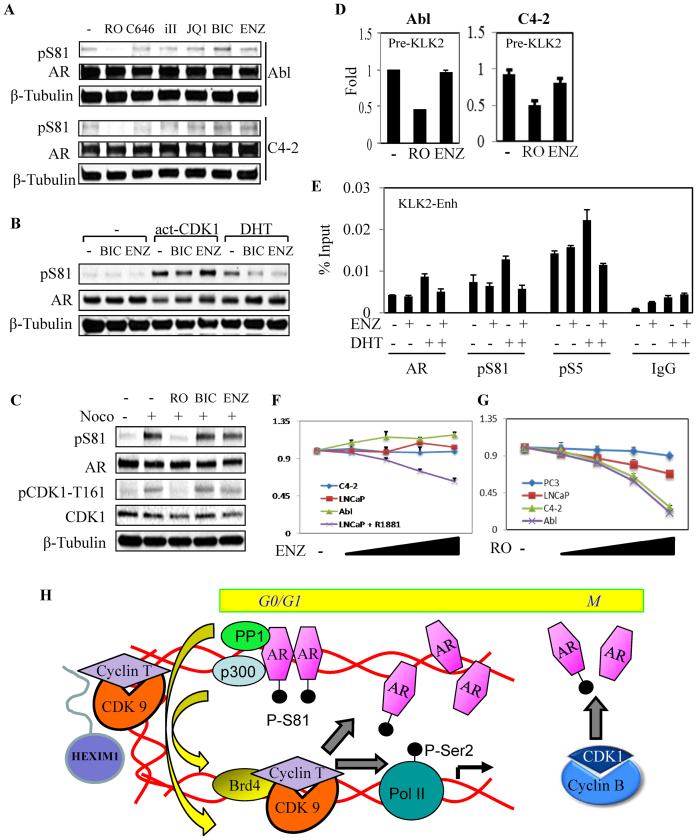
Figure 7.
CDK1-mediated basal pS81 and AR activation are not repressed by direct AR antagonists. (A) Abl and C4-2 cells in CDS medium were treated for 4 h with indicated compounds (CDK1 inhibitor RO-3306 (RO, 10 μM), p300 inhibitor (C646, 10 μM), CDK9 inhibitor (iII, 10 μM); BRD4 antagonist (JQ1, 500 nM), bicalutamide (BIC, 10 μM) and enzalutamide (ENZ, 10 μM) and total proteins were normalized for blotting. (B) 293T cells in CDS medium were co-transfected with AR, alone or with activated CDK1 (CDK-AF) and cyclin B1 vectors (23), followed by overnight treatments with bicalutamide (BIC, 10 μM), enzalutamide (ENZ, 10 μM) and DHT (10 nM) as indicated for blotting. (C) LNCaP cells in CDS medium were treated overnight with nocodazole (Noco, 50 ng/ml), followed by 4 h treatment with RO-3306, bicalutamide or enzalutamide (10 μM each) for blotting. (D) Abl and C4-2 cells in CDS medium were treated for 4 h with CDK1 inhibitor RO-3306 (10 μM) or enzalutamide (ENZ, 10 μM), followed by RNA isolation for qRT-PCR analysis of KLK2 pre-mRNA expression. (E) C4-2 cells in CDS medium were treated with enzalutamide (ENZ, 10 μM) and DHT (10 nM) as indicated for 4 h, followed by ChIP analysis. (F) LNCaP (without or with androgen as indicated), Abl and C4-2 cells in CDS medium were treated for 3 days with a range of doses of enzalutamide (0.4, 1, 2.5 and 10 μM), followed by cell proliferation analysis. The results were normalized to the untreated control that was set as 1. (G) Androgen-sensitive PCa cell line (LNCaP), CRPC cell lines (Abl and C4-2) and AR-negative PCa cell line (PC3) in CDS medium were treated for 3 days with a range of doses of RO-3306 (0.4, 1, 2.5 and 10 μM), followed by cell proliferation analysis. The results were normalized to the untreated control that was set as 1. (H) Proposed model for AR transcriptional activation. AR recruits PP1α to dephosphorylate and mobilize P-TEFb (CDK9/cyclin T) from an inhibitory 7SK complex, which can then phosphorylate RNA polymerase 2 (and associated proteins) for elongation and phosphorylate AR S81. The latter pS81 then enhances p300 binding, histone acetylation, BRD4 binding and further recruitment of P-TEFb to generate a positive feedback loop that sustains transcription of AR-regulated genes. CDK1 generates a basal pool of pSer81 that is needed to initiate this pathway, and increased CDK1-mediated pS81 phosphorylation may drive this pathway at very low androgen levels, or in the presence of AR antagonists, in CRPC.