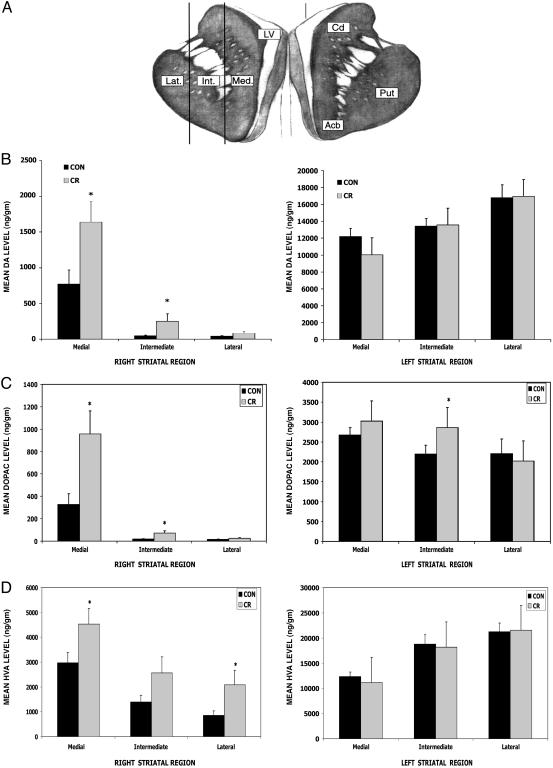
Fig. 3.
CR attenuates MPTP-induced depletion of DA and its metabolites in the striatum. (A) Concentrations of DA and its metabolites DOPAC and HVA were measured in tissue samples from three different regions of the striatum [lateral (Lat.), intermediate (Int.), and medial (Med.) regions] on both the left and right sides of the brain from MPTP-treated monkeys on the CR (n = 7) and control (n = 6) diets. Cd, caudate; Put, putamen; Acb, nucleus accumbens. (B–D) Measurements of levels of DA (B), DOPAC (C), and HVA (D) reveal that the CR monkeys had significantly higher DA levels in the medial (t = 2.5, df = 10; *, P = 0.016) and intermediate (t = 1.95, df = 6; *, P = 0.049) regions of the striatum compared with the control diet monkeys in the right striatum. (B) In the left (the side not receiving MPTP) striatum the DA levels were not significantly different between the CR and control diet groups (*, P > 0.05). (C) The CR group had significantly elevated DOPAC content in the intermediate region of the left striatum (t = 1.90, df = 10; *, P = 0.043). The DOPAC content was also significantly higher in both the medial (t = 2.76, df = 8; *, P = 0.012) and intermediate (t = 2.42, df = 6; *, P = 0.026) regions of the right striatum. (D) In the left striatum there was no significant diet effect on the HVA content (P > 0.05). In the right striatum, the HVA content was elevated significantly in both the medial (t = 2.06, df = 10; *, P = 0.033) and lateral regions (t = 2.02, df = 7; *, P = 0.042).