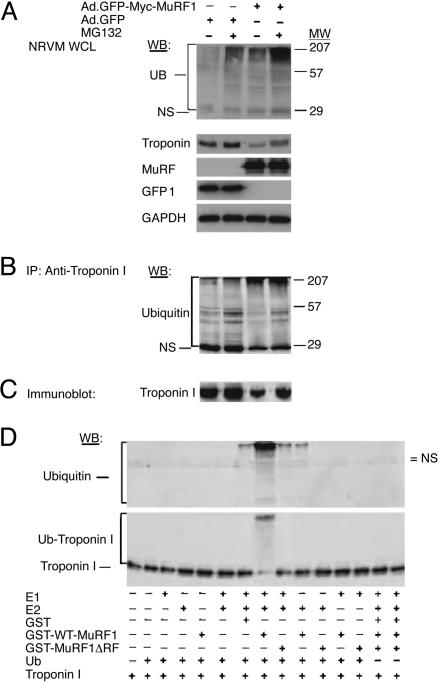
Fig. 4.
MuRF1 induces ubiquitylation of troponin I in vivo and in vitro. (A) NRVM were infected with Ad.GFP or Ad.GFP-Myc-MuRF1 and treated with MG-132 for 6 h. Ubiquitin (Ub) conjugates from lysates were separated by SDS/PAGE, and Western blotting (WB) was performed with an anti-ubiquitin Ab. Cell lysates were blotted simultaneously with anti-troponin I, anti-Myc, anti-GFP, and anti-GAPDH. NS, nonspecific; MW, molecular weight. (B and C) Lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-troponin I followed by immunoblotting with anti-ubiquitin (B) or were directly probed with anti-troponin I (C) Abs to detect ubiquitylated species of troponin I. (D) In vitro ubiquitylation reactions were performed to test the ubiquitin ligase activity of MuRF1. Ubiquitin conjugates of troponin I were detected with anti-ubiquitin (Upper) and anti-troponin I (Lower) Abs. The ubiquitylation of troponin I is noticeable as the accumulation of slower-migrating species of troponin I with concomitant loss of the ubiquitylated protein.