Figure 2.
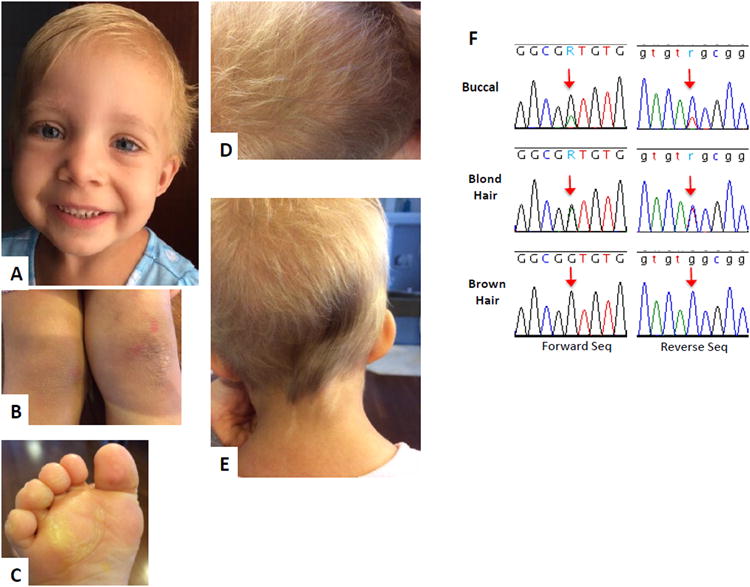
Clinical features of patient 5 and chromatogram of HRAS sequencing. A- Facial features at age 3 years 11 months, note high forehead and short blond hair, B- Hyperkeratosis on her knees, C-hyperkeratosis on her foot, D- scalp hair with a majority of short blond hairs and very few long brown hairs, E- scalp hair over her occiput showing the majority of blond hair with a patch of darker, longer and typical appearing hair, as well as streaky skin hypopigmentation compared to the relatively hyperpigmented surrounding skin of the neck. F- chromatogram of HRAS sequencing of the probands cheek swab derived DNA (labeled buccal) showing the more prominent wild type and the lesser mutant allele (arrow); the chromatogram for hair root cell derived DNA (labeled blond and brown, respectively) showing 50% mutant allele (blond hair, arrow) or only wild type allele (brown hair, arrow), respectively.
