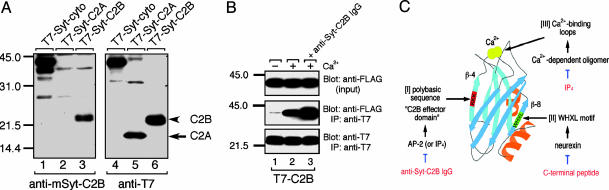
Fig. 1.
Characterization of the anti-mSyt I-C2B antibody. (A) Immunoblots showing the specificity of the anti-mSyt I-C2B with the total homogenates of COS-7 cells expressing T7-Syt I-cyto, T7-Syt I-C2A, or T7-Syt I-C2B. Recombinant T7-tagged Syts were subjected to SDS/12.5% PAGE and transferred to a poly(vinylidene difluoride) membrane. The blots were first probed with the anti-mSyt I-C2B antibody (0.5 μg/ml; Left). The same blots were stripped and reprobed with HRP-conjugated anti-T7 tag antibody (1/10,000 dilution) to ensure loading of the same amounts of T7-Syt proteins (Right). Note that the anti-mSyt I-C2B antibody specifically recognized the C2B domain (lane 3), but not the C2A domain (lane 2), even after prolonged exposure to x-ray film (data not shown). (B) Effect of the anti-mSyt I-C2B antibody on Ca2+-dependent oligomerization of the C2B domain. Purified T7-mSyt I-C2B domain (Bottom) was coupled with the anti-T7 tag antibody-conjugated agarose and incubated with FLAG-Syt cytoplasmic domain in the presence of 2 mM EGTA (lane 1) or 1 mM Ca2+ (lanes 2 and 3) (30, 31). After the beads were washed extensively, proteins bound to the beads were analyzed by SDS/12.5% PAGE, followed by immunoblotting with HRP-conjugated anti-FLAG tag antibody (Middle). Input means 1/80 volume of the reaction mixture (Top). Note that the anti-mSyt I-C2B antibody (10 μg) did not inhibit Ca2+-depenent oligomerization of the C2B domain (Lane 3, Middle); instead, it promoted oligomerization. The positions of the molecular mass markers (× 10-3) are shown on the left. (C) Schematic representation of the three distinct ligand-binding sites of the C2B domain (5, 25).