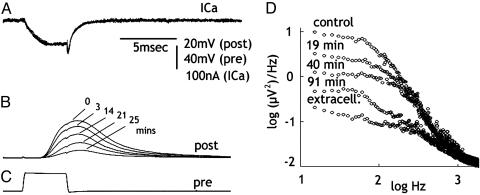
Fig. 3.
IgG injection reduces transmitter release and spontaneous synaptic noise without modifying inward Ca2+ current. (A-C) Reduction of transmitter release (B) after a presynaptic voltage-clamp pulse (C) at different times after IgG injection. Note the lack of change in ICa (A). (D) Postsynaptic noise measurements at different times after IgG injection. Control before injection, extracellular noise level with the postsynaptic electrode outside the post axon is shown.