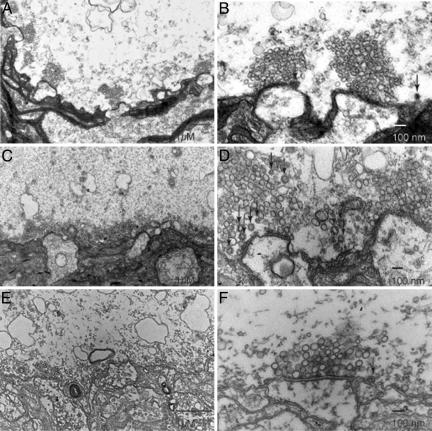
Fig. 5.
Presynaptic injection of anti-mSyt I-C2B results in decreased number of CCVs. Ultrastructure of the giant squid synapse identifying the pre- and postsynaptic structures. (A and B) Electron micrographs from cross sections of nonstimulated, noninjected control synapse. (A) A low-magnification image displaying several active zones with large clusters. (B) Higher-magnification image illustrating the large number of vesicles and number of CCVs (arrows). (C and D) Electron micrographs from cross sections of stimulated, noninjected control synapse to illustrate the effect of stimulation on vesicular number and morphological properties. (C) Low-magnification image showing a decreased number of vesicles during stimulation. (D) An increase in CCVs displayed in higher magnification (arrows). (E and F) Electron micrographs from cross sections of stimulated, anti-mSyt I-C2B-injected synapse. (E) Low-magnification images, demonstrating the significant decreases in vesicle number. (F) Display of low number of CCVs in anti-mSyt I-C2B-injected terminals. Arrows identify clathrin-coated vesicles in B, D, and F.