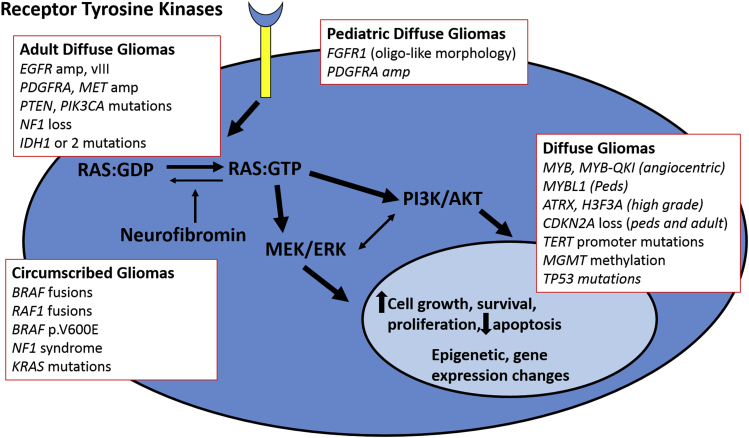
Figure 1.
Signaling pathways relevant to glial neoplasms in adults and children. A variety of signaling pathways are activated through mutations of oncogenes or tumor suppressor genes in diffuse gliomas in adults and children. MAPK pathway activation through receptor tyrosine kinase activation or downstream gene mutations and rearrangements (BRAF, NF1, RAS) is a universal feature of glial neoplasms. The PI3K/mTOR pathway is also activated through receptor tyrosine kinase activation and downstream gene mutations (PTEN, PI3KCA). Other relevant alterations include mutations affecting metabolic and epigenetic pathways (IDH1, IDH2, H3F3A) and telomere activity and/or maintenance (TERT, ATRX). Although there is some overlap regarding the pathways activated in adult and pediatric gliomas, the specific alterations and/or frequencies differ in these two broad subgroups. ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; MEK, mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase.