Figure 2.
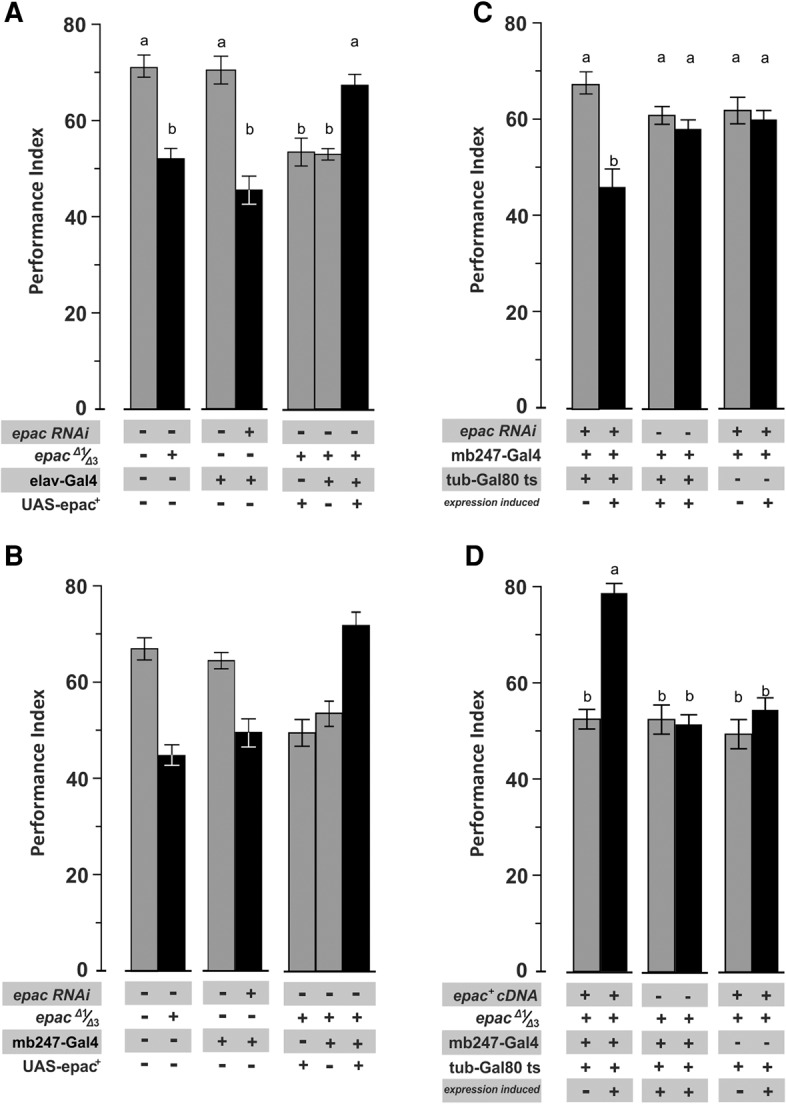
Epac supports STM formation at the level of the mushroom body Kenyon cells. Genetic manipulation of EPAC function determines STM performance. (A) Pan-neuronal expression of an epac-specific RNAi transgene mimics performance of null epac mutants, while pan-neuronal rescue restores performance to wild-type levels. (B) Restricting expression of transgenes to the mushroom body by means of mb247-Gal4 identifies Kenyon cells as a necessary and sufficient section of EPAC function to support STM. (C) Induced EPAC knockdown at the adult stage by means of the TARGET system excludes developmental contributions to loss of STM. (D) Induced EPAC rescue at the adult stage restores STM performance. All data represent means ± SEM. N = 6–8. Statistical differences at the level of P ≤ 0.05 are denoted by different letters.
