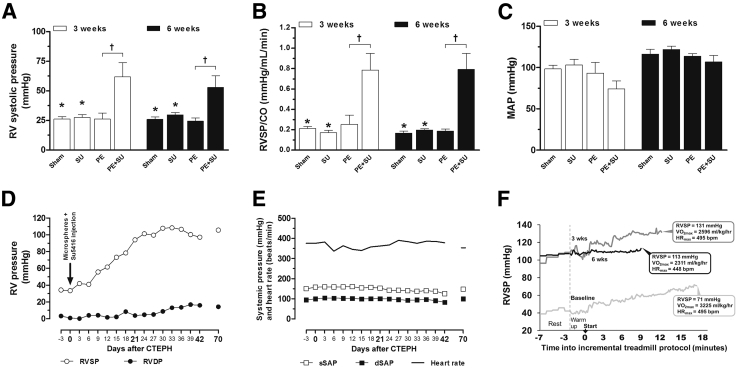
Figure 1.
In vivo hemodynamics assessment data on early stage (3 weeks) and late stage (6 weeks). Measurements from admittance catheter placed in the right ventricle (RV) of anesthetized rats (A–C), and a conscious, freely moving rat implanted with telemetry system transmitting real-time data from indwelling pressure-sensing catheters (D and F). A: RV systolic pressure (RVSP). B: Index of pulmonary vascular resistance [RVSP normalized by cardiac output (CO)]. C: Mean arterial pressure (MAP). D: RV pressures (systolic and diastolic). E: Systemic pressures (systolic and diastolic) and heart rate. F: Real-time RVSP tracings recorded in the telemetrically instrumented animal during VO2max testing performed at baseline (light gray line) and at 3 weeks (dark gray line) and 6 weeks (black line) after PE + SU induction. Five minutes of resting collection on a stationary treadmill belt (rest), and a 2-minute warm-up period (warm up) preceded the start (arrow) of the incremental treadmill protocol in 3-minute stages. Maximal oxygen uptake (VO2max, in mL/kg/hour), and maximal heart rate (HRmax, in bpm) are indicated in call-out boxes at each test's termination point (time to exhaustion) in addition to maximal RVSP. Values are expressed as means ± SEM (A–C). n = 4 (3 weeks; A–C); n = 4 to 6 (6 weeks; A–C). ∗P < 0.05 versus PE + SU group; †P < 0.05 versus PE group. CTEPH, chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension; dSAP, diastolic–systemic arterial pressure; HR, heart rate; RVDP, RV diastolic pressure; sSAP, systolic–systemic arterial pressure.