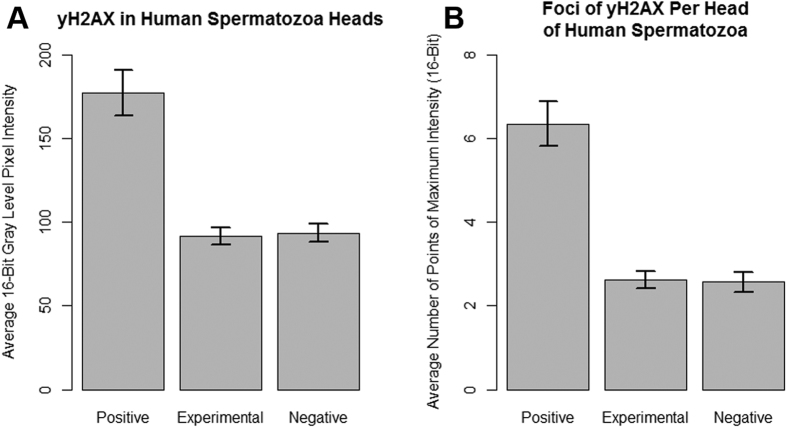
Figure 4. Quantification of double-strand DNA breaks in sperm using γH2AX.
The mean pixel intensities and number of foci were determined using ImageJ software. Error bars indicate standard deviation. Data is representative of n = 82, n = 127, and n = 88 sperm heads for the positive, experimental, and negative groups, respectively. (A) A Kruskal-Wallis test determined that there was no statistical significance between the mean pixel intensities of the experimental and negative control groups (p = 0.6605). The mean pixel intensity of the positive control group was determined to be significantly higher than that of the experimental and negative control groups (p = 2.144 × 10−10). The mean pixel intensities for the positive, experimental, and negative groups were 177.4, 93.5, and 91.9, respectively. (B) A Kruskal-Wallis test indicated that the positive control had much larger numbers of γH2AX foci than the other two groups (p = 1.474 × 10−10). The numbers of γH2AX foci in the heads of sperm in the experimental group and negative control group were compared using a Kruskal-Wallis test (p = 0.723). The average number of γH2AX foci in the positive, experimental, and negative groups were 6.4, 2.6 and 2.6, respectively.