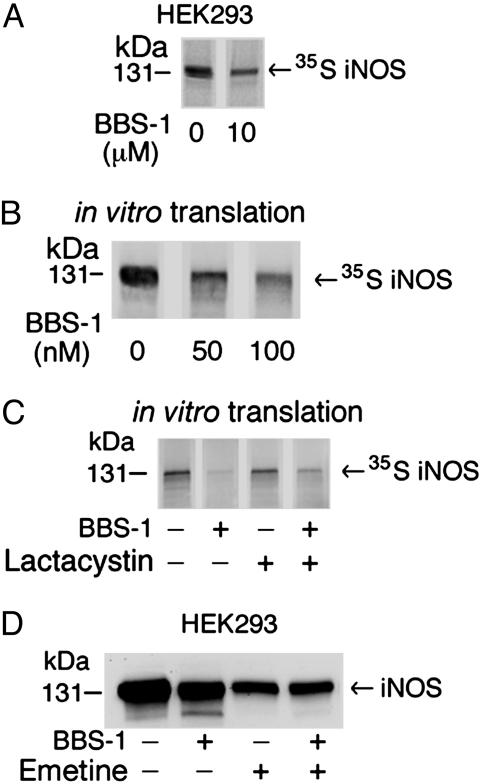
Fig. 7.
Effect of BBS-1 on iNOS translation in cultured cells and in vitro.(A) HEK 293 cells, stably expressing iNOS, were labeled by [35S]methionine/cysteine mix for 1 h in the presence or absence of 10 μM BBS-1. iNOS was immunoprecipitated from cell lysates with anti-iNOS antibody. Eluted proteins were separated by SDS/PAGE, and bands, representing 35S-labeled iNOS, were detected by PhosphorImager. (B) Rabbit reticulocyte-based in vitro coupled transcription/translation system and iNOS cDNA plasmid were used to express human iNOS in the presence of 0–100 nM BBS-1. Reactions were performed at 30°C for 90 min. Translation products were separated by SDS/PAGE, and bands, representing 35S-labeled iNOS, were detected by PhosphorImager. (C) In vitro translation of iNOS was done in the presence of BBS-1(10 μM), in the presence or absence of the proteasome inhibitor lactacystin (10 μM). (D) HEK 293 cells, stably expressing iNOS, were incubated for 8 h in the presence or absence of BBS-1 (10 μM) or the translation inhibitor emetine (20 μM). Western blotting of cell lysates (50 μg per lane) was performed by using an anti-iNOS antibody.