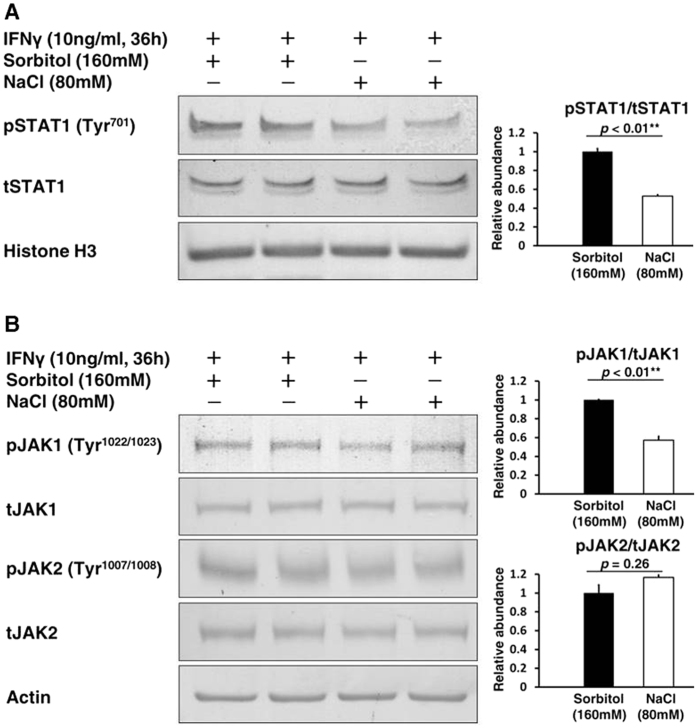
Figure 4. Suppression of the JAK-STAT signaling pathway in HK2 cells exposed to a high salt concentration.
The cells were treated by IFNγ (10 ng/mL) for 36 h after a 2 h exposure of culture medium supplemented with either NaCl (80 mM) or Sorbitol (160 mM, as an osmotic control). (A) Left, Representative immunoblotting performed to evaluate the phosphorylation of STAT1 in the nucleus; Right, Densitometry analysis of the immunoblotting of the phosphorylation of STAT1 in the nucleus (n = 5). Full-length western blot images are presented in Supplementary Figure S2. A high salt concentration inhibited phosphorylation of STAT1 at tyrosine 701 in the nucleus. (B) Left, Representative immunoblotting performed to evaluate the phosphorylation of JAK1 and JAK2; Right-upper, Densitometry analysis of the immunoblotting of the phosphorylation of JAK1 (n = 4); Right-lower, Densitometry analysis of the immunoblotting of the phosphorylation of JAK2 (n = 4). Full-length western blot images are presented in Supplementary Figure S3. A high salt concentration also inhibited phosphorylation of JAK1 at tyrosine 1022/1023, but not phosphorylation of JAK2 at tyrosine 1007/1008.