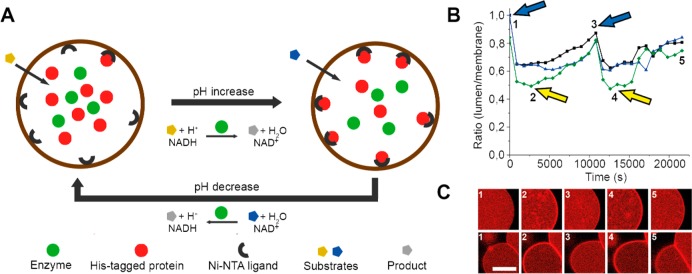
Figure 4.
Reversible assembly of a His-tagged protein on the membrane of a GUV. The assembly is driven by the catalytic activity of ADH, which changes the pH of the vesicle’s lumen. (A) Schematic of the reversible assembly. (B) Alternating addition of two substrates (indicated by arrows) drives membrane assembly and disassembly of the His-tagged protein. (C) Fluorescence microscopy images of GUVs corresponding to the time points in panel B. Adapted with permission from ref (35). Copyright 2015 Wiley.