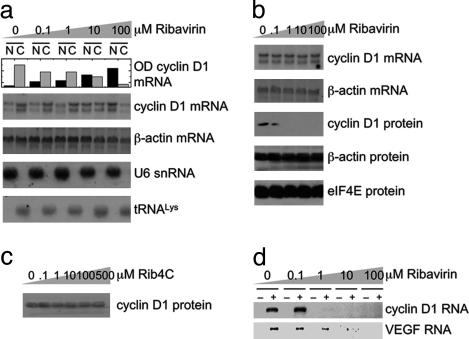
Fig. 2.
Ribavirin specifically inhibits eIF4E:mRNA binding, inhibits nucleocytoplasmic mRNA transport, and depletes levels of transport-regulated proteins. (a) Northern blots of RNA extracts of nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions of ribavirin-treated NIH 3T3 cells, which were probed as indicated. U6 small nuclear RNA and tRNALys serve as controls for quality of the fractionation. Ribavirin inhibits nucleocytoplasmic mRNA transport of cyclin D1, but not β-actin, with an apparent EC50 of ≈1 μM, as judged from the bar graph quantification (top row). N, nuclear; C, cytoplasmic. This effect was confirmed by using quantitative real-time PCR (Fig. 6b). (b) Northern and Western blots of total extracts of ribavirin-treated cells, exhibiting depletion of cyclin D1, without affecting transcription, mRNA stability, and protein synthesis. (c) Western blot of total protein extract of Rib4C-treated cells that were probed for cyclin D1. (d) Semiquantitative RT-PCR of cyclin D1 mRNA contained in eIF4E purified from the nuclei of ribavirin-treated cells. Control samples were purified by using IgG antibody (–) instead of antibody specific for eIF4E (+). Semiquantitative PCR of VEGF from cytoplasmic extracts was immunopurified as above.