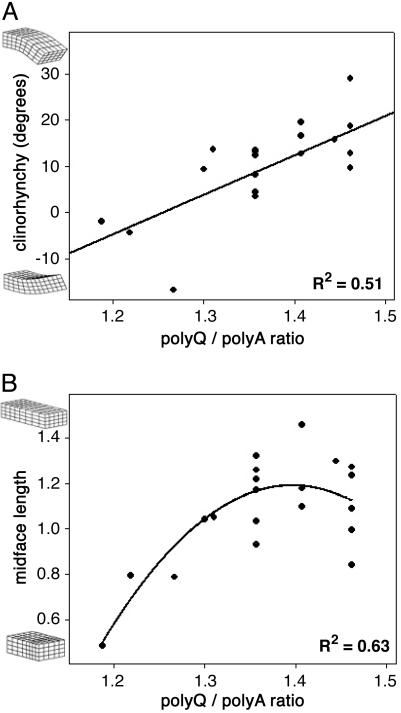
Fig. 2.
Tandem repeat length in a developmental gene is quantitatively correlated with continuous morphological features. (A and B) Reported (9, 11) effects on transcription of polyglutamine and polyalanine repeats suggested that these two domains may be involved in competitive activities and that the relative lengths of these domains may be more instructive than their aggregate length. A Pearson correlation test of this hypothesis revealed a significant correlation between Runx-2 polyglutamine to polyalanine ratio and clinorhynchy (D/V nose bend, P = 0.0001, Pearson one-sided significance, n = 27, A) and midface length (P = 0.0002, n = 27, B) (24). The nature and direction of these correlations is indicative of longer relative Runx-2 glutamine repeats resulting in increased midface growth, consistent with observations from human cleidocranial dysplasia patients (25). Published studies (9–16) indicate that amino acid repeat length-function relationships are typically nonlinear; however, fitting a quadratic or exponential to the clinorhynchy data (A) does not provide sufficient improvement in residuals to support the use of a nonlinear function over a simple line.