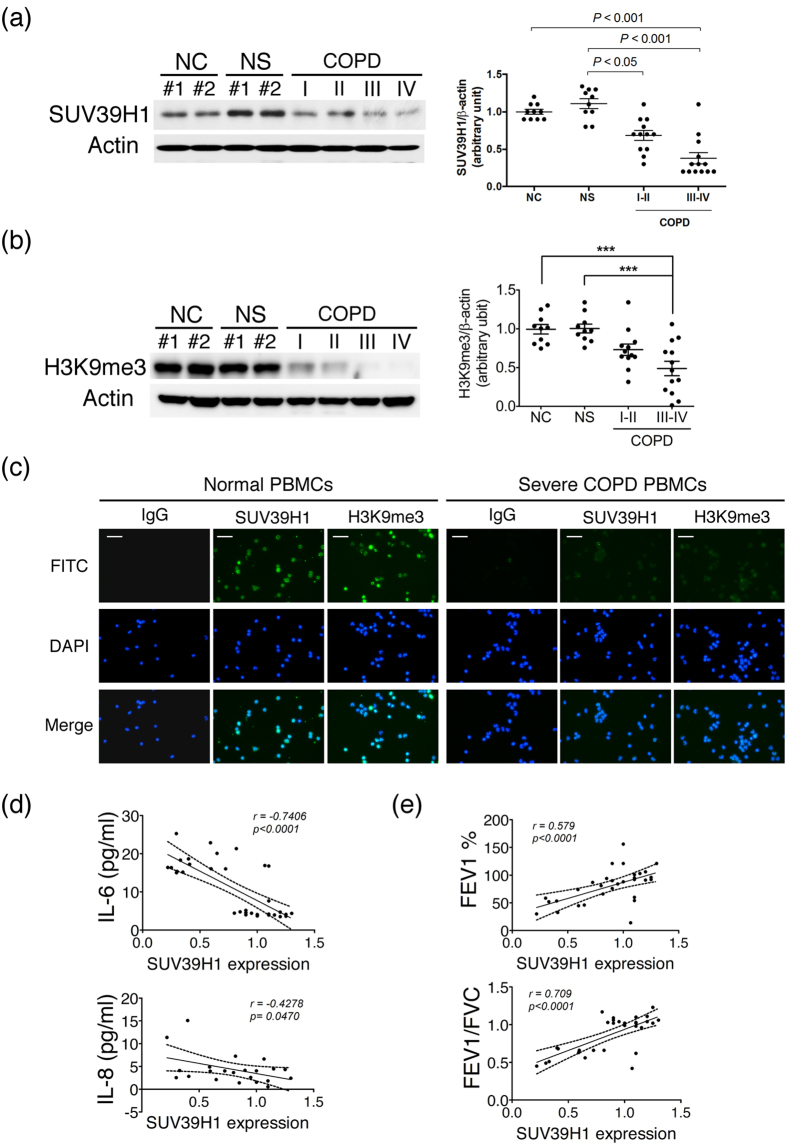
Figure 1. SUV39H1 and H3K9me3 levels are reduced in peripheral blood mononuclear cells(PBMCs) from chronic obstructive pulmonary disease(COPD) subjects.
The protein expression in PBMC samples from normal control subjects(NC), normal smoking subjects(NS), and COPD patients were measured by immunoblot.(a) The SUV39H1 expression levels were significantly reduced in COPD PBMCs compared with normal or smoking subjects. Actin served as a loading control. Densitometry values for SUV39H1 were normalized to actin. Values were expressed as the fold change over control.(b) The global H3K9me3 levels were also diminished in COPD PBMCs.(c) Cytospin preparations from freshly isolated PBMCs from normal or severe COPD subjects stained for SUV39H1 and H3K9me3(green color). Cell nuclei were visualized using DAPI(blue color). Isotype controls remained negative, original magnification ×200. All data are presented as the mean ± SEM of at least three independent experiments.(d) A significant correlation was observed between the IL-6 and SUV39H1 levels of serum and PBMC samples in all subjects(upper panel). IL-8 levels are associated with SUV39H1 expression in normal non-smoking controls and COPD patients(lower panel).(e) Correlation between pulmonary function parameters FEV1 or FEV1/FVC and SUV39H1 in all subjects. The undetermined values of IL-8 are excluded from the analysis. Scale bar, 200 μm. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; and ***p < 0.001.