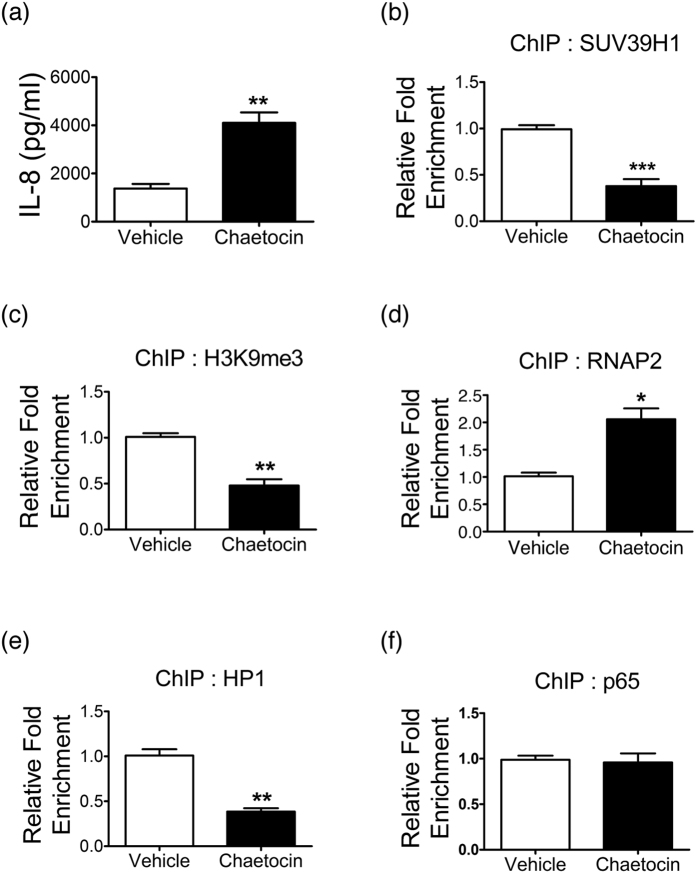
Figure 5. SUV39H1 inhibition is involved in the epigenetic modulation of the IL-8 gene.
(a) Normal human small airway epithelial cells(HSAEpCs) were treated with chaetocin(100 nM) for 16 hours, and IL-8 protein levels were evaluated by ELISA analysis.(b) The recruitment of SUV39H1 in the IL-8 gene promoter was markedly reduced in HSAEpCs with SUV39H1 inhibitor(chaetocin) treatment compared with vehicle control(DMSO). The enrichment of SUV39H1 was evaluated by chromatin immunoprecipitation(ChIP) analysis.(c) The enrichment of H3K9me3 in the IL-8 gene promoter was also decreased via the inhibition of SUV39H1 methyltransferase activity.(d) The IL8 levels were increased. Accordingly, the recruitment of RNA polymerase II(RNAP2) in IL-8 gene promoter was robustly increased.(e) Similar to SUV39H1 modulation, the SUV39H1-interacting partner, HP1 was decreased in the epigenetic regulation complex with the blockade of SUV39H1 activity.(f) However, the enrichment of NF-κB subunit p65 was not significantly elevated in the IL-8 gene promoter. All data are presented as the mean ± SEM of at least three independent experiments. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; and ***p < 0.001.