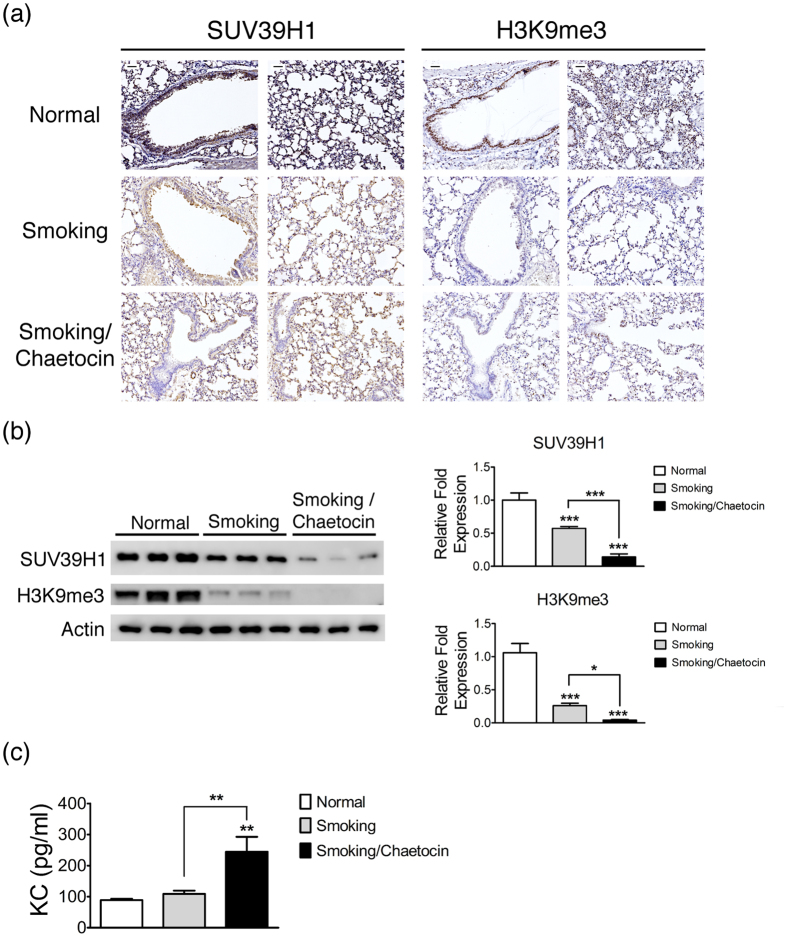
Figure 7. SUV39H1 repression increases the inflammation response in cigarette smoke exposure mice.
(a) SUV39H1 or H3k9me3 levels were visualized by immunohistochemical staining in the lungs of cigarette smoke filtered control(normal), cigarette smoke exposure(smoking), or smoking combined with chaetocin administration(smoking/chaetocin) mice. Smoking and smoking/chaetocin mice displayed slightly and markedly reduced SUV39H1 expression in the epithelium compared with control mice, respectively. The H3K9me3 levels were also considerably decreased in smoking and smoking/chaetocin mice. Scale bar, 200 μm.(b) Western blot analysis of SUV39H1 or H3k9me3 showed a similar trend as the immunohistochemical staining results. The H3k9me3 levels were significantly reduced in smoking and smoking/chaetocin mice compared with control mice.(c) Chaetocin treatment accelerates the protein levels of a murine IL-8 homologue, KC, in the lung tissue induced by smoking. The KC expression of the smoking(gray bars) or smoking and chaetocin(black bars) treated mice(n = 6 animals per group) is depicted compared with control mice. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; and ***p < 0.001.