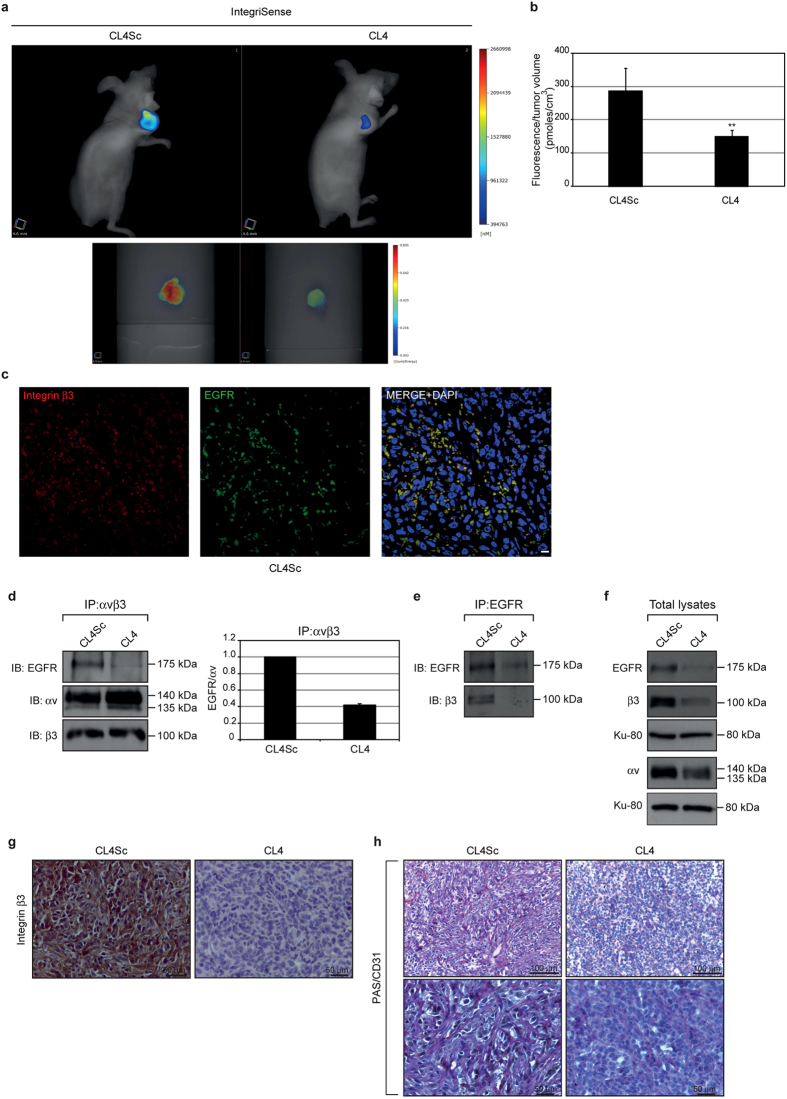
Figure 6. CL4 decreases IntegriSense signal in tumors and inhibits VM.
(a,b) In vivo imaging and quantification of IntegriSense in tumor-bearing mice. (a) Representative volume renderings taken at the same color gating from CL4Sc- and CL4-treated mice injected with IntegriSense at day 21 (upper panels). Representative images of the single tumors excised from CL4Sc- and CL4-treated mice after in vivo imaging (lower panels). (b) The amount of fluorescence (pmoles) was quantified in specific ROIs encompassing the tumor in the animal and normalized to tumor volume (cm3). Error bars depict means ± SD. P = 0.0091 (n = 4). (c) Representative sections of tumors (CL4Sc group) were stained with anti-integrin β3 (red) and anti-EGFR (green) antibodies and analysed by confocal microscopy. Nuclei were stained with DAPI. Co-localization results appear yellow in the merged image. Magnification 63×, scale bar = 10 μm. (d–f) Equal amounts of lysates from recovered tumors were immunoprecipitated with anti-integrin αvβ3 LM609 antibody (d) or anti-EGFR antibody (e) and immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. Total lysates were immunoblotted with anti-EGFR, anti-integrin αv and anti-integrin β3 antibodies, as indicated. Equal loading was confirmed by immunoblot with anti-Ku-80 antibody (f). Molecular weights of indicated proteins are reported. Representative data are shown from one of three independent experiments. In d, the histogram reports the amount of EGFR co-immunoprecipitated with integrin αvβ3 relative to αv levels. Values are shown relative to CL4Sc control, arbitrarily set to 1. (g,h) Representative sections of tumors harvested from CL4Sc and CL4 groups were stained with integrin β3 (g) and PAS/CD31 (h) as indicated. (Magnification 40×, scale bar = 50 μm; Magnification 20×, scale bar = 100 μm).