Extended Data Figure 6. ME3 depletion in ME2 null cells causes mitochondrial dysfunction.
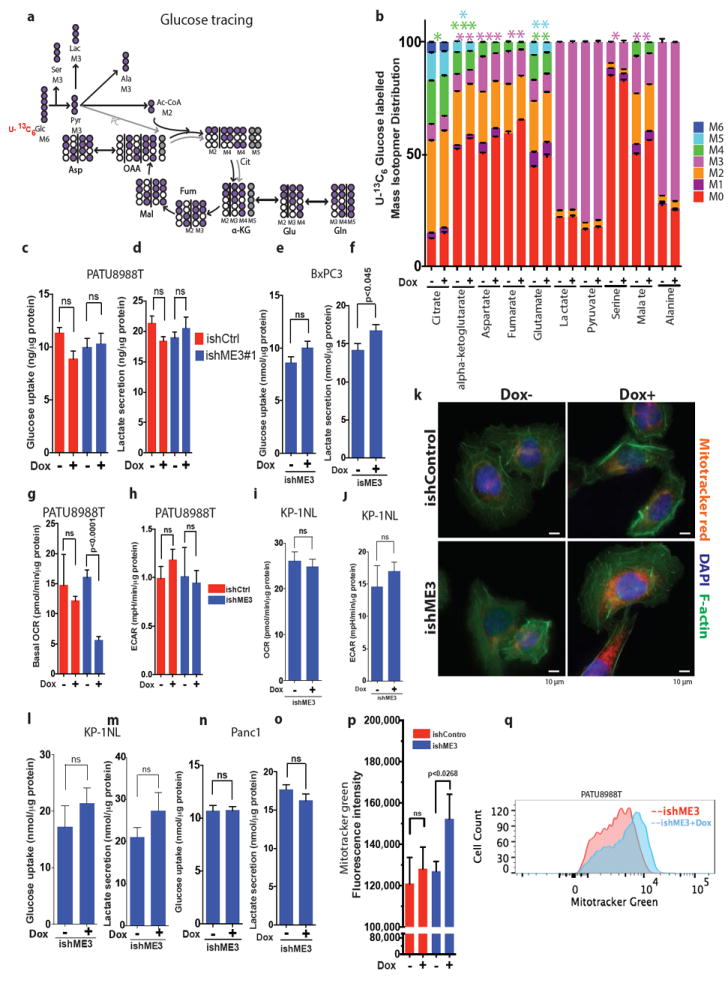
a, Mapping of carbon atom transitions using uniformly labelled 13C6-glucose. b, MID of uniformly labelled 13C6-glucose contribution to TCA cycle metabolites. ME3 depletion led to decreased glucose entry to TCA cycle. Error bars represent the s.e.m of n = 4 biological samples from two independent experiments. P values were determined by two-tailed t-test. c–f, Glucose uptake rate and lactate secretion rate were measured in PATU8988T (c, d) and BxPC3 (e, f) cells. g, h, Measurements of oxygen consumption rate (OCR) (g) and extracellular acidification rate (ECAR) (h) in PATU8988T cells upon ME3 depletion. i, j, Measurements of OCR (i) and ECAR (j) in KP-1NL cells upon ME3 depletion. Error bars represent s.e.m. of at least n = 5 replicates. P values were determined by two-tailed t-test. k, MitoTracker red, DAPI and F-actin staining of ME3-depleted (Dox+) and non-depleted (Dox–) cells. l–o, Glucose uptake rate and lactate secretion rate were measured in KP-1NL (l, m) and Panc1 (n, o) cells. p, Quantification of MitoTracker green staining to assess the mitochondrial biomass (Scale bar= 10 μm). q, Representative flow cytometry data of MitoTracker green staining of ME3-depleted (+Dox) versus. non-depleted cells. Error bars represent s.e.m. of at least n = 5 replicates. P values were determined by two-tailed t-test.
