Figure 4. ME3 regulates BCAT2 expression via AMPK and its downstream effectors.
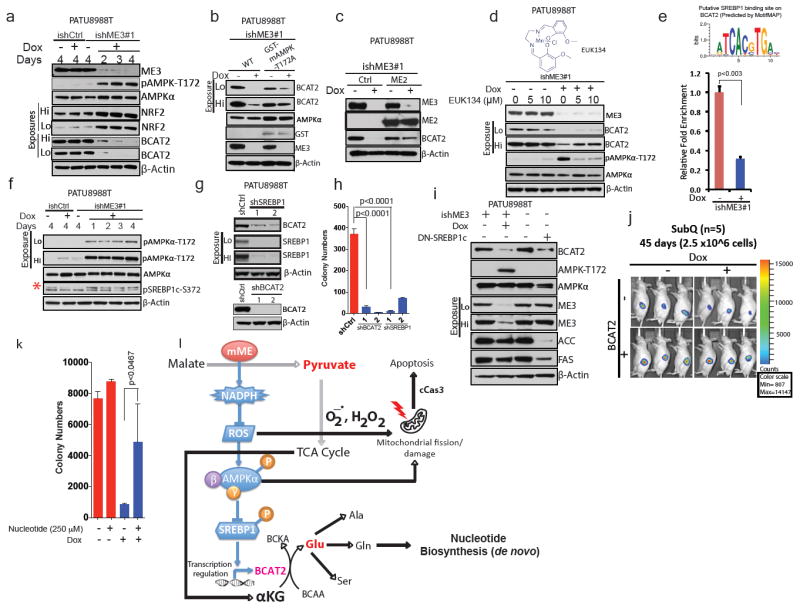
a, Immunoblot assessing activation of AMPK and expression of NRF2 in PATU8988T cells. β-Actin used as loading control. (b) Immunoblot showing rescue of BCAT2 expression using GST-tagged kinase-dead AMPK (T172A) in PATU8988T cells. c, Immunoblot showing rescue of BCAT2 expression by ME2 in PATU8988T cells. d, Immunoblot showing rescue of BCAT2 expression by 24-h treatment with EUK134. e, Top, putative SREBP1-binding site on BCAT2 promoter predicted by MotifMAP. Bottom, chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) analysis of SREBP1 binding to BCAT2 promoter. f, Immunoblot of SREBP1c phosphorylation at S372 in PATU8988T cells (Red asterisk denote the specific band). g, Immunoblot of BCAT2 expression upon shRNA-mediated depletion of SREBP1 (top) and BCAT2 (bottom) in PATU8988T cells. h, Colony formation assay of cells depleted in BCAT2 (shBCAT2) or SREBP1 (shSREBP1). i, Immunoblot assessing BCAT2 expression in PATU8988T cells expressing DN-SREBP1c (Y320A). j, Luciferase images of BCAT2-overexpressing subcutaneous tumours (n = 5 each group) 45 days after implantation of 2.5 × 106 cells. Colour scale, minimum 807, maximum 14,147. k, Rescue of ME3-depleted cells by addition of nucleotides. l, Proposed model of mitochondrial malic enzyme (mME) function. β-Actin used as loading control in all immunoblots. Error bars represent s.d. of at least three replicates. P values determined by two-tailed t-test.
