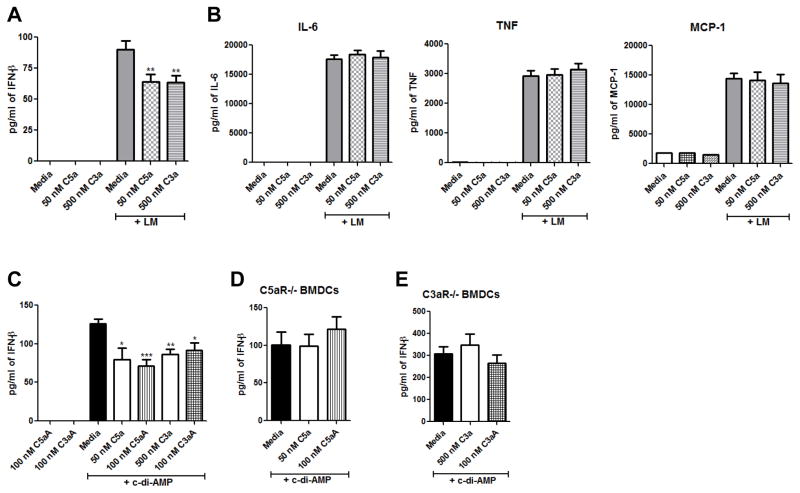
Figure 2. C5a and C3a suppress IFN-β production in BMDCs.
WT BMDCs were pre-treated with either media, 50 nM C5a, or 500 nM C3a for 2 h, and then the cells were infected with Lm overnight. Cell-free supernatants were used to quantitate (A) IFN-β production or (B) IL-6, TNF-α, and MCP-1 production. (C) WT BMDCs were pre-treated with either media, 50 nM C5a, 100 nM C5aA, 500 nM C3a, or 100 nM C3aA for 2 h and then were incubated with 25 μg/ml c-di-AMP for 20 h. IFN-β was quantitated from cell-free supernatants. (D) C5aR−/− BMDCs were pre-treated with either media, 50 nM C5a, or 100 nM C5aA for 2 h and (E) C3aR−/− BMDCs were pre-treated with either media, 500 nM C3a, or 100 nM C3aA for 2 h, and then the cells were incubated with 25 μg/ml c-di-AMP for 20 h. IFN-β was quantitated from cell-free supernatants. All data are presented as mean pg/ml ± SEM. These data are pooled from three independent experiments. * P ≤ 0.017; ** P ≤ 0.009; *** P = 0.0006 by t test.