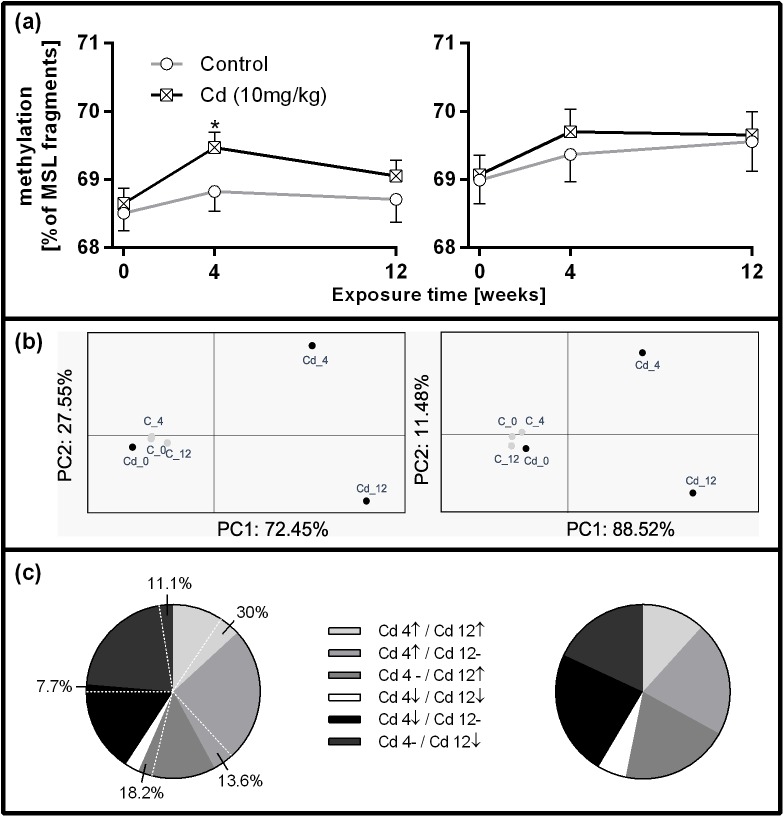
Fig 5. Methylation changes in L. terrestris coelomocytes in controls (C) (grey lines) and individuals exposed to soil spiked with 10 mg/kg CdCl2 (Cd) (black lines).
Left and right panels refer to replica I and II, respectively. Only fragments where methylation did not change in the control treatment were considered for analysis. (a) Percentage of methylated fragments among all methylation states in MSL fragments in replica I (407 MSL) and replica II (463 MSL), between control and Cd-treated earthworms. (b) Principal co-ordinate analysis was performed using the data on the epigenetic distance of differentially methylated MSL between treatment groups in replica I (76 MSL) and replica II (94 MSL). (c) Type of DNA methylation change among differentially methylated MSL in replica I (76 MSL) and replica II (94 MSL). The percentages of the left pie chart indicate fragments which showed the same methylation changes after 7 months in clean soil. ↑ indicates an increase and ↓ a decrease in methylation compared to Cd 0 (earthworms used for Cd exposure sampled before the exposure start),—indicates that methylation returned to the Cd 0 level; Cd 4/Cd 12: earthworms sampled after 4 or after 12 weeks of exposure to 10 mg/kg CdCl2.