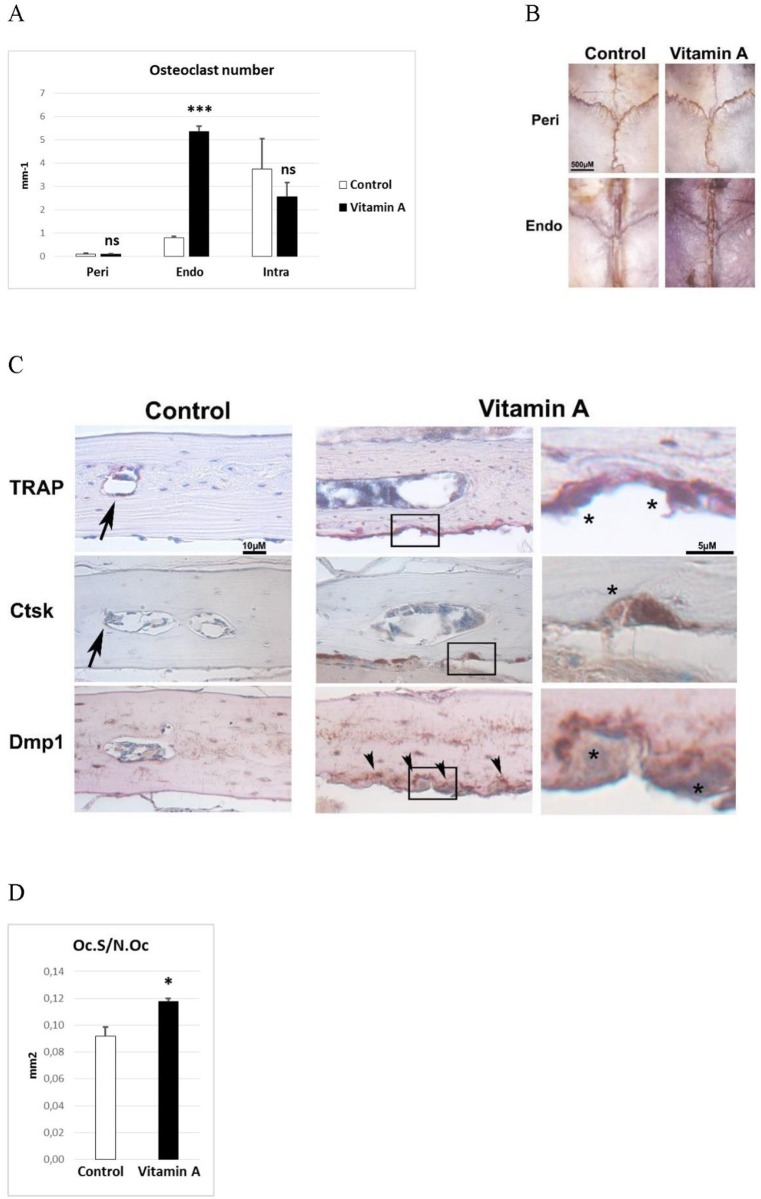
Fig 2. The osteoclast phenotype.
A) Osteoclast number from histomorphometric analysis of pericranial (Peri), endocranial (Endo) and intracranial (Intra) surfaces (n = 4/group). B) Tartrate resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP) stained (red) intact calvaria. Photograph from pericranial (Peri) and endocranial (Endo) side. C) Representative pictures of TRAP staining (red) and immunohistochemical staining (brown) for cathepsin K (Ctsk) and dentin matrix protein 1 (Dmp1) of decalcified calvaria sections. Arrows indicate small, flat osteoclasts (TRAP and Ctsk) present in control tissue. Arrowheads indicate Dmp1 staining close to the endocranial osteoclasts, only found in bone from vitamin A animals. Right panel under “Vitamin A” shows high power pictures of boxed areas where asterisks indicate large osteoclasts only found in vitamin A animals. D) Osteoclast size determined as the osteoclast surface (Oc.S) divided by the osteoclast number (N.Oc) (n = 4/group). Results are given as means + SD. ns = not statistically significant, * p < 0.05 and *** p < 0.001.