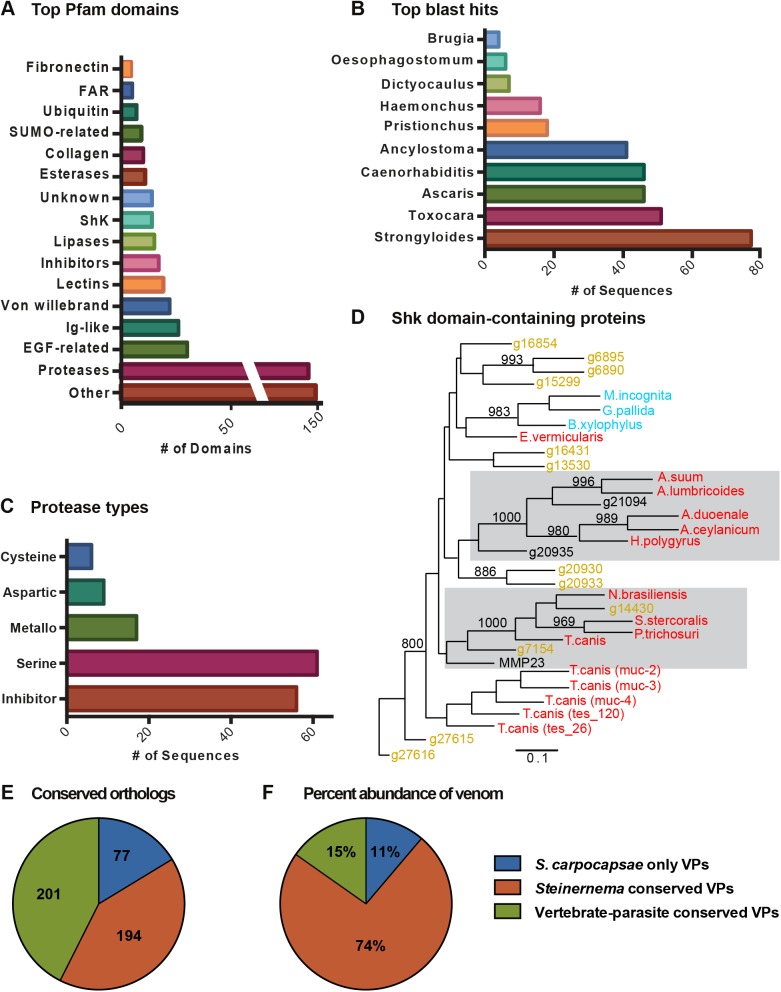
Fig 6. Comparative analysis of venom proteins from activated IJs.
(A) Top BLAST hits of the 472 venom proteins in non-Steinernema organisms. (B) The top 16 Pfam domains in the venom proteins. (C) Merops breakdown of proteases and protease inhibitors found in the venom. (D) A neighbor-joining gene tree of the Shk domain-containing proteins found in the venom. Gray boxes highlight S. carpocapsae proteins with high similarity to Shk domain-containing proteins of vertebrate-parasitic nematodes. Bootstrap values of more than 80% (from 1000 replicates) are indicated at nodes. Bar, 10% divergence. (E) A pie chart showing the number of venom proteins that are conserved with at least one vertebrate-parasitic nematode, conserved with at least one other species of Steinernema, or are specific to S. carpocapsae. (F) A pie chart showing the percentage of molecules in the venom that belong to each of the categories above (conserved with at least one vertebrate-parasitic nematode, conserved with at least one other species of Steinernema, or specific to S. carpocapsae).