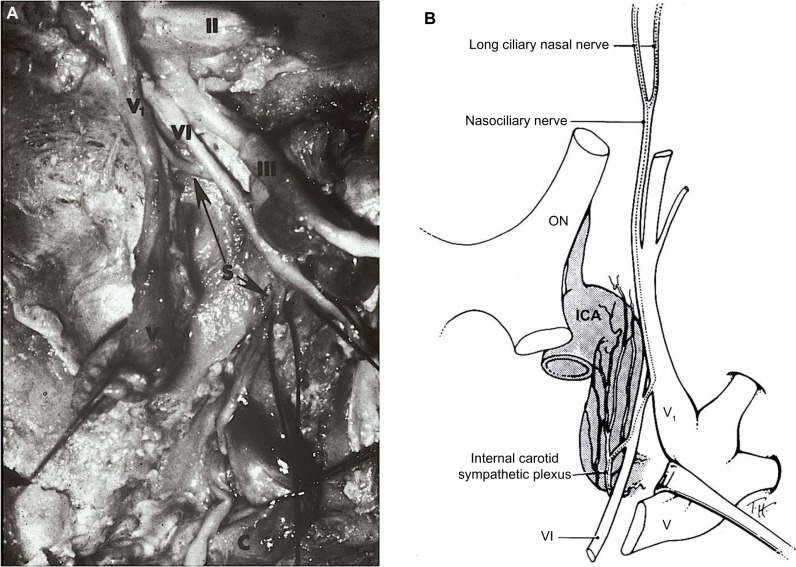
Figure 3.
(A) Cadaver dissection showing oculosympathetic fibers (S) attaching (lower arrow) to the abducens nerve (VI) within the cavernous sinus. After running with the nerve for a short distance, they separate from the nerve (upper arrow) and join with the first division of the trigeminal nerve (V1) to enter the orbit.
Notes: II, optic nerve; III, oculomotor nerve; V, trigeminal ganglion. Copyright © 1978 Wiley-Liss, Inc. Adapted with permission from Parkinson D, Johnston J, Chaudhuri A. Sympathetic connections to the fifth and sixth cranial nerves. Anat Rec. Wiley Publishers. 1978;191:221–226.49 (B) Artist’s drawing showing that the post-ganglionic oculosympathetic fibers briefly travel with the abducens nerve (VI) before joining the ophthalmic division (V1) of the trigeminal nerve. Thereafter, the sympathetic fibers enter the orbit with its nasociliary branch. Copyright © 2005, Lippincott Williams. Adapted with permission from Kardon R. Anatomy and physiology of the autonomic nervous system. In: Miller NR, Biousse V, Kerrison JB, editors. Walsh and Hoyt’s Clinical Neuro-Ophthalmology. 6th ed. Baltimore, MD, USA: Lippincott-Williams & Wilkins; 2005.134
Abbreviations: ON, optic nerve; ICA, internal carotid artery.