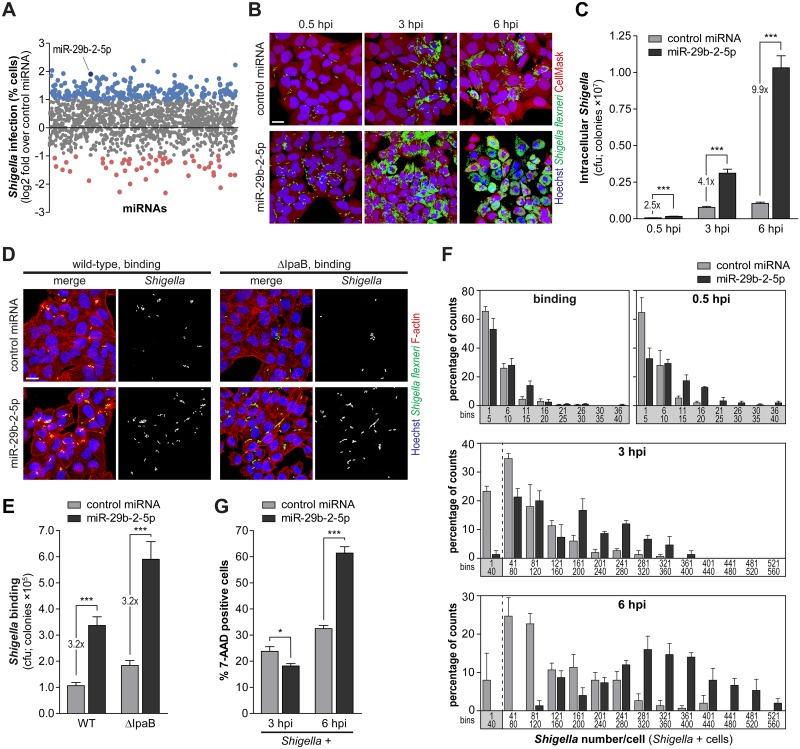
Fig 1. MiR-29b-2-5p favors Shigella binding and intracellular replication.
A. Effect of human miRNA mimics (genome-wide library of miRNA mimics corresponding to miRBase 19) on the percentage of Shigella infected cells (expressed as log2 fold change compared to control miRNA). MiRNAs highlighted in blue and red significantly increase or decrease infection by at least 2-fold, respectively (P<0.05). B and C. Representative images (B) and cfu quantification (C) of intracellular bacteria in HeLa cells infected with Shigella WT, upon treatment with miR-29b-2-5p or control miRNA mimics, and analyzed at three times post-infection (0.5, 3 and 6 hpi). Scale bar, 20 μm. D and E. Representative images (D) and cfu quantification (E) of bacteria bound to HeLa cells transfected with miR-29b-2-5p or control miRNA mimics and incubated with Shigella WT or ΔIpaB mutant strain for 10 min. Scale bar, 20 μm. F. Distribution of the number of Shigella per infected cell at different times post-infection (binding, 0.5, 3 and 6 hpi), in HeLa cells transfected with miR-29b-2-5p or control miRNA mimics. Results are shown for at least 50 infected cells per condition and independent experiment. Values in the X-axis correspond to the extremities of the defined bins. G. Percentage of 7-AAD positive cells following treatment with miR-29b-2-5p or control miRNA mimics for the cell population with internalized Shigella (Shigella +), analyzed at 3 and 6 hpi. Shigella infection was performed at MOI 10, except for the binding experiments (panels D and E) in which MOI 50 was used. Results are shown as mean ± s.e.m. from 4 (panel F), 5 (panels C and E) or 15 (panel G) independent experiments; *P<0.05, ***P<0.001.