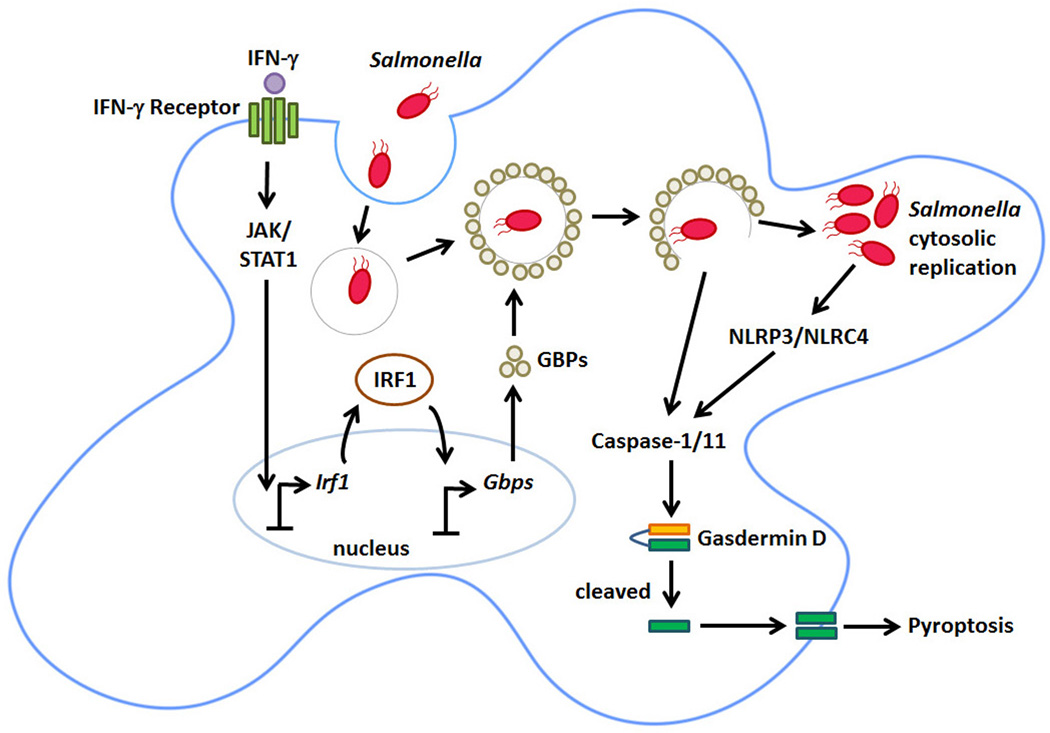
Figure 2. IFN-γ control of Salmonella lifecycle in phagocytic cells.
Salmonella is phagocytosed by the macrophage and immediately forms an SCV to survive in the unfavorable acidic environment of the cell. IFN-γ leads to JAK/STAT1 dependent IRF1 induction and transcription of GBPs, which localize to the SCV, lysing it. Upon lysis, Salmonella is released into the cytosol of the macrophage where the bacterium is recognized by the inflammasome sensors NLRC4 and NLRP3, which activate caspase-1/11. In parallel, cytosolic LPS can be directly sensed by caspase-11. Once activated, these caspases cleave Gasdermin D. The N-terminal cleavage product of Gasdermin D then localizes to and punctures holes in the plasma membrane, triggering pyroptotic death.