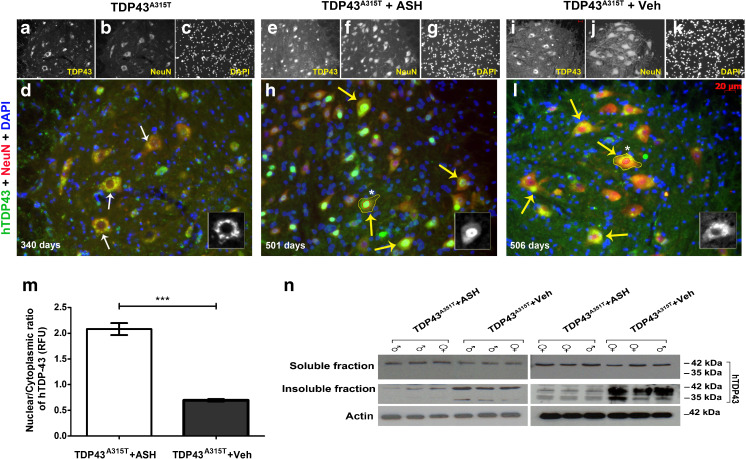
Fig. 6.
Alleviation of human transactive response DNA binding protein 43 (hTDP-43) mislocalization and aggregation in Ashwagandha (ASH)-treated hTDP-43A315T mice. In hTDP-43A315T mice, there is a clear nuclear depletion of hTDP-43 occurring in spinal motor neurons at about 11 months of age (a–d). Therefore, ASH treatment was initiated after this age. After 8 weeks of treatment, the spinal cord of hTDP-43A315T mice (~500 days old) exhibited intense immunodetection of hTDP-43 in the nucleus of motor neurons (e–h). In contrast, the Veh-treated mice exhibited diffused hTDP-43 in the cytoplasm of spinal cord neurons (i–l). All images are of 20× magnification. Scale bar = 20 μm. The single-channel images are grayscale so as to give better contrast. The merged colored images are 150% enlargements. (Inset) A single cell with hTDP-43 staining has been enlarged to 300%. Nuclear:cytoplasmic hTDP-43 stain intensity was calculated from motor neurons (neurons with diameter ≥4 μm) present in ventral horn of spinal cord sections using ImageJ after demarcation of the nuclear (outline drawn in red) and whole cell area (outline drawn in yellow) using 4,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) in Adobe Photoshop. Results showed a significant increase of about 3.5-fold in the nuclear to cytoplasmic ratio in ASH-treated spinal motor neurons compared with Veh-treated samples (m). Data were analyzed by 2-tailed t test with Welch’s correction (***p < 0.001). On subjecting detergent-soluble and insoluble fractions of spinal cord lysate to immunoblotting, no major difference was observed in the soluble hTDP-43 levels between the 2 groups. However, hTDP-43 was present at lower levels in the insoluble fraction of ASH-treated hTDP-43A315T mice when compared with Veh-treated hTDP-43A315T mice. ASH treatment caused also a reduction in levels of the toxic 35-kDa TDP-43 species (cleaved fragment/splice variant) (n)