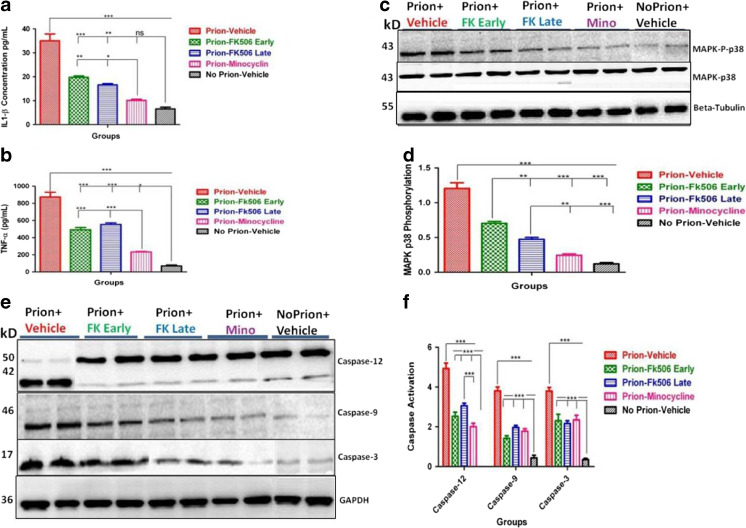
Fig. 6.
Minocycline (Mino) modulates the caspase-dependent mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway. (a) Level of interleukin (IL)-1β in brain homogenates of 3 animals per group detected using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Data were analyzed by 1-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Tukey’s multiple comparison post-test (***p < 0.0001). (b) Level of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α in brain homogenates of 3 animals per group detected using ELISA. Data were analyzed by 1-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison post-test (***p < 0.0001). (c) Representative Western blots of 2 animals each from every group for protein expression of MAPK phosphorylated p38 level and total MAPK p38 level in comparison with β-tubulin (third panel). (d) Expression level of MAPK phosphorylated p38 in brain homogenates of 5 animals each per group. Data were analyzed by 1-way ANOVA test with Tukey’s multiple comparison post-test (***p < 0.0001). (e) Representative Western blots of 2 animals per group for caspase-12, caspase-9, and caspase-3. (f) Levels of activated caspase-12, caspase-9, and caspase-3 in brain homogenates of 5 animals each per group. Data were analyzed by 2-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post-test (***p < 0.001). ns = nonsignificant