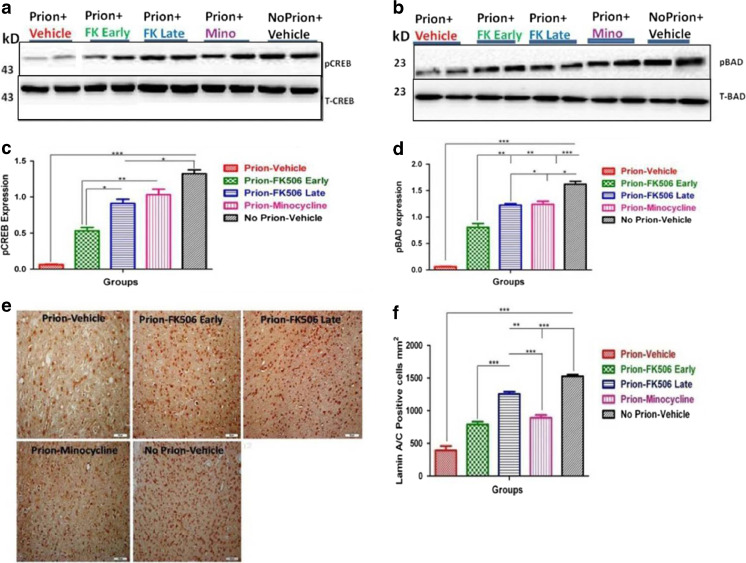
Fig. 8.
Minocycline (Mino) increases cognition and survival via cyclic adenosine monophosphate response element-binding (CREB) and Bcl-associated death promoter (BAD) phosphorylation. (a) Representative Western blot panel of 2 animals from each group for total CREB and phosphorylated CREB levels. (b) Representative Western blot panel of 2 animals from each group for total BAD and phosphorylated BAD levels. (c) Protein expression level of phosphorylated CREB in different groups based on 5 animals data per group. Data were analyzed by 1-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Tukey’s multiple comparison post-test (***p < 0.0001). (d) Protein expression level of phosphorylated BAD in different groups based on data from 5 animals per group. Data were analyzed by 1-way ANOVA test with Tukey’s multiple comparison post-test (***p < 0.0001). (e) Representative pictures of immunohistochemical analysis for the expression of lamin A/C protein in different groups. (f) Protein expression levels of lamin A/C for apoptosis analysis in different experimental groups based on 5 animals per group. Data were analyzed by 1-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison post-test (***p < 0.0001)