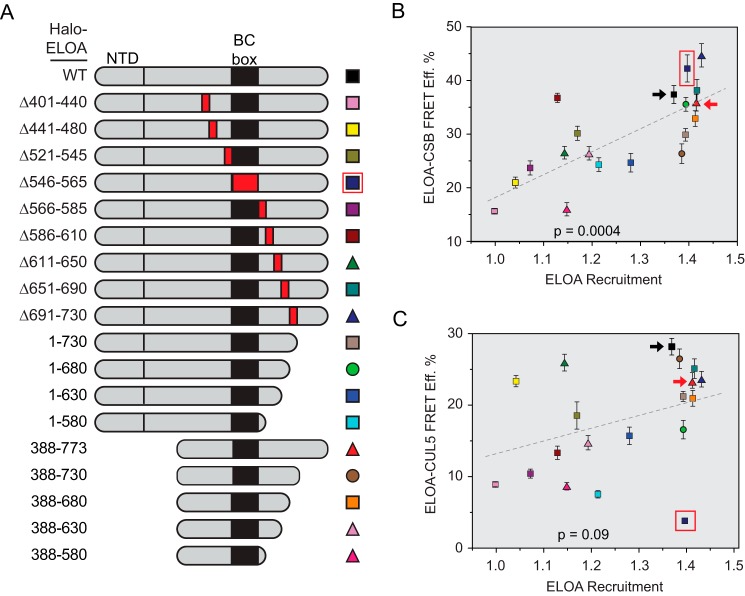
Figure 3.
Effects of Elongin A mutations on CSB or CUL5 binding and recruitment to DNA damage. A, schematic representation of wild-type and mutant Elongin As. Red boxes indicate positions of internal deletions. Halo-ELOA, Halo-tagged Elongin A; NTD, N-terminal domain. B and C, Elongin A-CSB or Elongin A-CUL5 AP-FRET efficiency (FRET Eff.) versus Elongin A recruitment. AP-FRET efficiency is expressed as mean ± S.E.; Elongin A recruitment is the Rt value measured at 30 s after microirradiation. p values are for comparison of the slopes of the linear regressions to a zero slope. Black arrows highlight wild-type Elongin A, red arrows highlight the Elongin A(388–773) mutant, which lacks the TFIIS- and MED26-like N-terminal domain, and a red box highlights Elongin A(Δ546–565), which lacks the BC-box.