Figure 2.
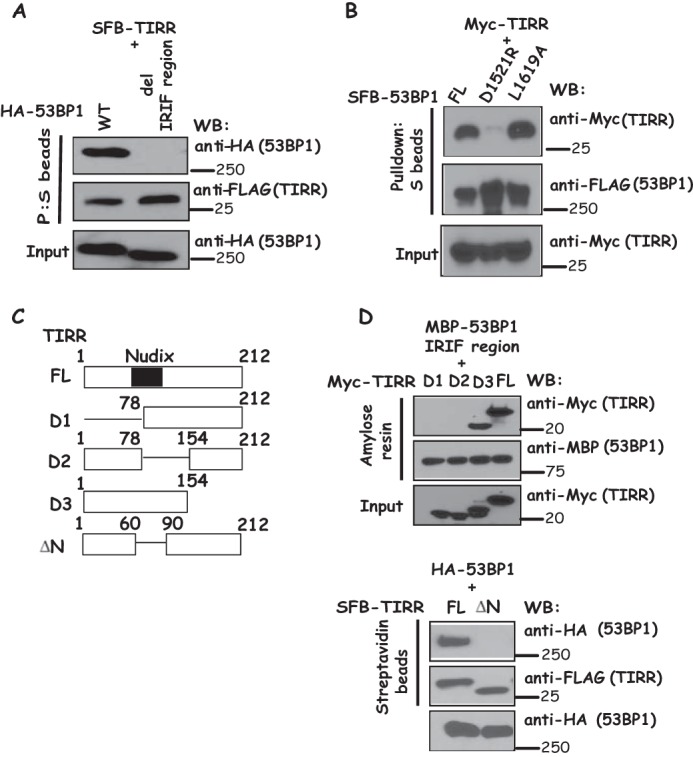
Mapping the binding regions on 53BP1 and TIRR. A, 53BP1 IRIF region is required for 53BP1-TIRR interaction. 293T cells were transfected with plasmids encoding SFB-tagged TIRR together with plasmids encoding wild-type or IRIF region deletion mutant of HA-tagged 53BP1. Immunoprecipitation reactions were conducted using S-protein beads and then subjected to Western blotting (WB) using the indicated antibodies. B, disruption of the Tudor domain of 53BP1 decreased the binding of 53BP1 to TIRR. 293T cells were transfected with plasmids encoding SFB-tagged TIRR together with plasmids encoding wild-type, D1521R, and L1619A mutant of HA-tagged 53BP1, respectively. Immunoprecipitation reactions were conducted using S-protein beads and then subjected to Western blotting using indicated antibodies. C, schematic presentation of wild-type and deletion mutants of TIRR used in this study. Nudix domain is indicated as a blue rectangle (residues 60–90). D, Nudix motif of TIRR is required for its binding to 53BP1. Beads coated with bacterially expressed MBP-fused 53BP1 IRIF region were incubated with cell lysates containing exogenously expressed Myc-tagged wild-type or deletion mutants of TIRR. Moreover, 293T cells were transfected with plasmids encoding HA-tagged 53BP1 together with plasmids encoding wild-type deletion mutants of SFB-tagged TIRR. Immunoprecipitation reactions were conducted using S-protein beads. Immunoblotting experiments were carried out using indicated antibodies.
