Figure 7.
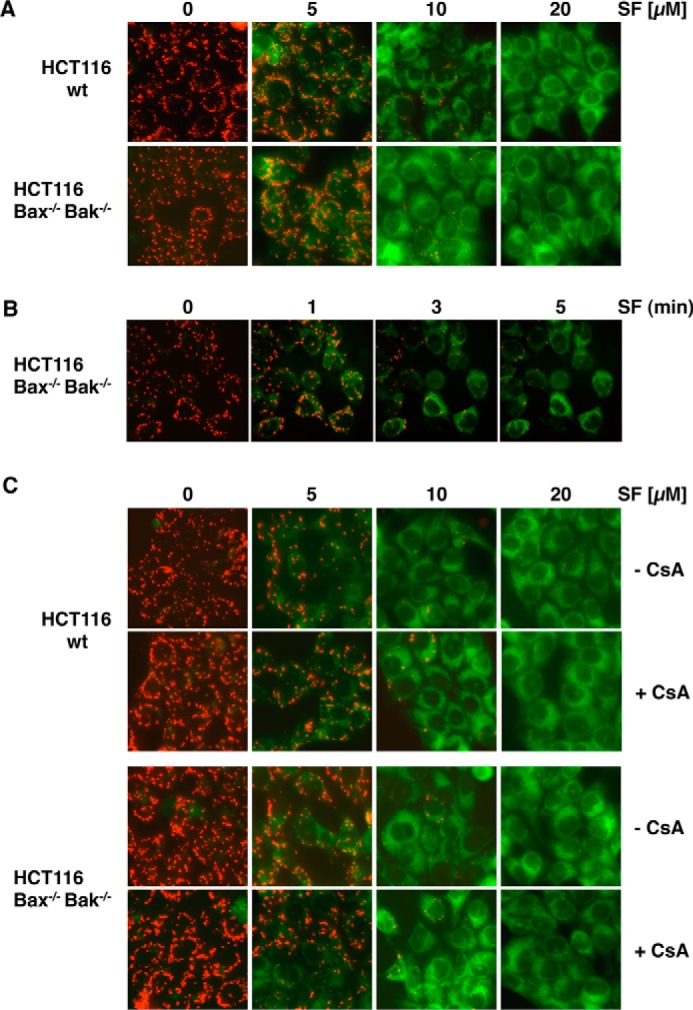
Sorafenib-induced mitochondrial depolarization upon sorafenib/TRAIL treatment is independent of Bax and Bak and the MPTP. A, HCT116-WT cells and isogenic HCT116-Bax−/−/Bak−/− cells were treated with sorafenib and stained with JC-1 to analyze loss of mitochondrial membrane potential. Fluorescence microscopy (top panels) showed decreased red and increased green fluorescence upon treatment with sorafenib in both cell lines, indicating that loss of ΔΨm is independent of Bax and Bak. B, HCT116-Bax−/−/Bak−/− cells were treated with sorafenib for the indicated time periods and stained with JC-1. Loss of ΔΨm is detectable 1–3 min after treatment in almost all cells. C, in addition to sorafenib, HCT116-WT and HCT116-Bax−/−/Bak−/− cells were preincubated with CsA to block MPTP opening. Upon treatment, cells were stained with JC-1 and analyzed by fluorescence microscopy. CsA failed to prevent sorafenib-induced mitochondrial depolarization in HCT116-WT and HCT116-Bax−/−/Bak−/− cells, demonstrating that sorafenib-induced depolarization is independent of both MPTP and Bax/Bak.
