Figure 2.
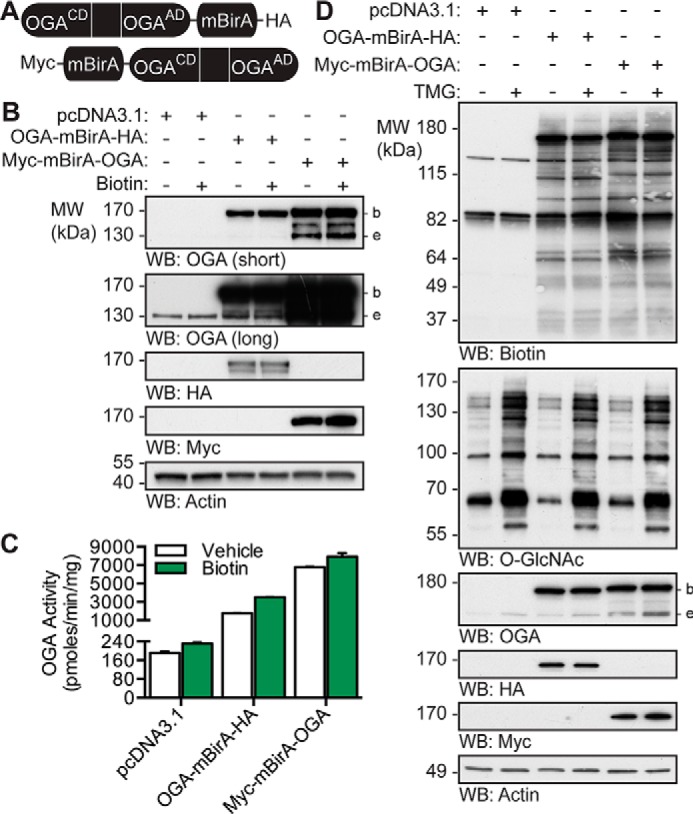
OGA-mBirA fusion proteins express, maintain catalytic activity, and biotinylate proteins in vivo. A, schematic of the OGA-mBirA fusion proteins. CD and AD represent the catalytic (β-N-acetylglucosaminidase) domain and acetyltransferase-like domain of OGA, respectively. B–D, U2OS cells were transfected with pcDNA3.1, OGA-mBirA-HA, or Myc-mBirA-OGA and treated with or without biotin (25 μm, 16 h) or TMG (100 nm, 20 h) as indicated. Proteins were extracted in TCL buffer. B, equal amounts of protein (10 μg) were separated by SDS-PAGE, and the following were detected by Western blotting: OGA, HA, Myc, and actin. n = 3. C, desalted lysates were assayed for OGA activity using 4MU-GlcNAc (1 mm). n = 3, representative data from one experiment is shown. Error bars indicate the intra-assay standard deviation from two technical replicates. D, equal amounts of protein (4.5 μg) were separated by SDS-PAGE, and the following were detected by Western blotting: biotin, O-GlcNAc, OGA, HA, Myc, and actin. n = 2. Migration of endogenous OGA (e), mBirA-tagged OGA (b), and the molecular mass (MW) markers are indicated.
