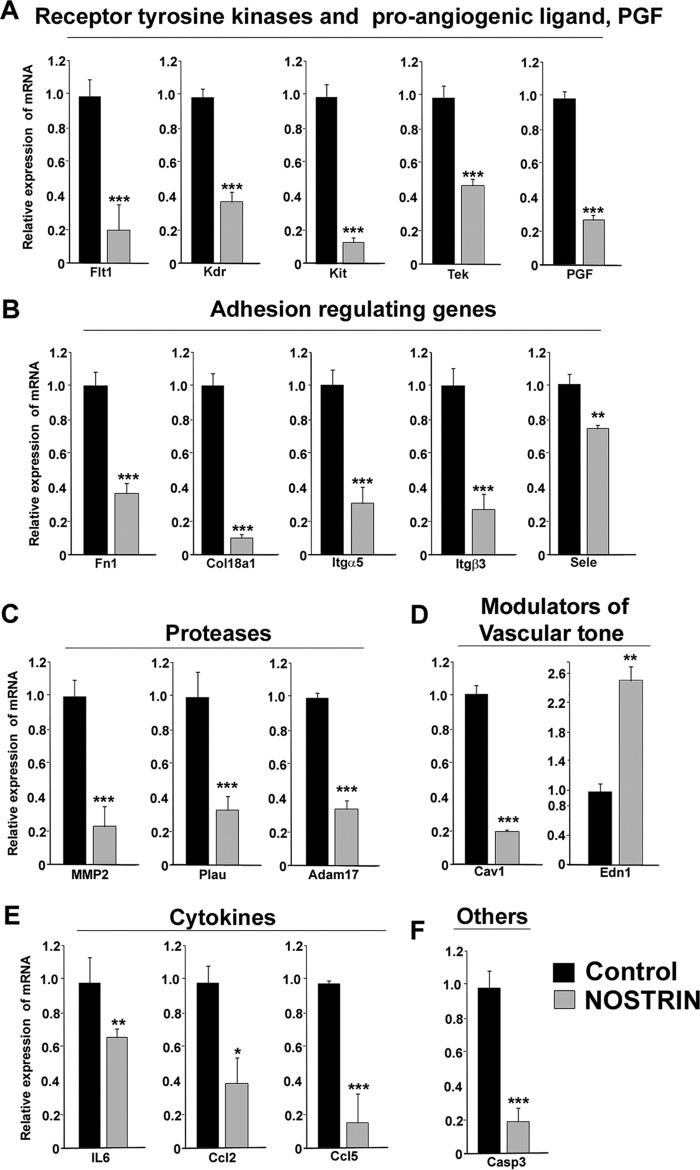
Figure 3.
Real-time PCR analysis of transcripts in endothelial cells affected by aberrant NOSTRIN expression. Quantitative real-time PCR analysis of endothelial function-associated genes shows significant differences in Nostrin-overexpressed versus control endothelial cells. The amount of a specific mRNA was normalized relative to the amount of rpL7 (ΔCt = Ctgene − CtrpL7). The -fold change of gene expression was measured by using 2−ΔΔCt, where ΔΔCt denotes the change in ΔCt values between samples and reference sample (here, vector backbone-transfected endothelial cells sample was used as the reference sample, ΔΔCt = ΔCtgene_NOSTRIN − ΔCtgene_control). Error bars represent S.E. from three different biological replicates. A, the receptor tyrosine kinases including Flt-1, Kdr, Kit, and Tek along with the pro-angiogeneic ligand Pgf, which can bind to Flt-1, were down-regulated significantly with overexpression of NOSTRIN. B, NOSTRIN overexpression led to significant down-regulation of transcripts of several genes involved in adhesion and invasion such as Fn1, Col18a1, Itgα5, Itgβ3, and Sele. C, expression of the three proteases Mmp-2, Plau, and Adam-17 was found to be diminished remarkably by NOSTRIN overexpression. D, Cav1, a well-known regulator of vascular tone, was down-regulated, whereas Edn-1, a vasoconstrictor, was up-regulated significantly by NOSTRIN overexpression. E, a significant decrease in mRNA levels of cytokines such as IL6, Ccl2, and Ccl5 was induced by NOSTRIN overexpression. F, Casp3, which induces apoptosis, was found to be down-regulated on NOSTRIN overexpression. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; and ***, p < 0.005.