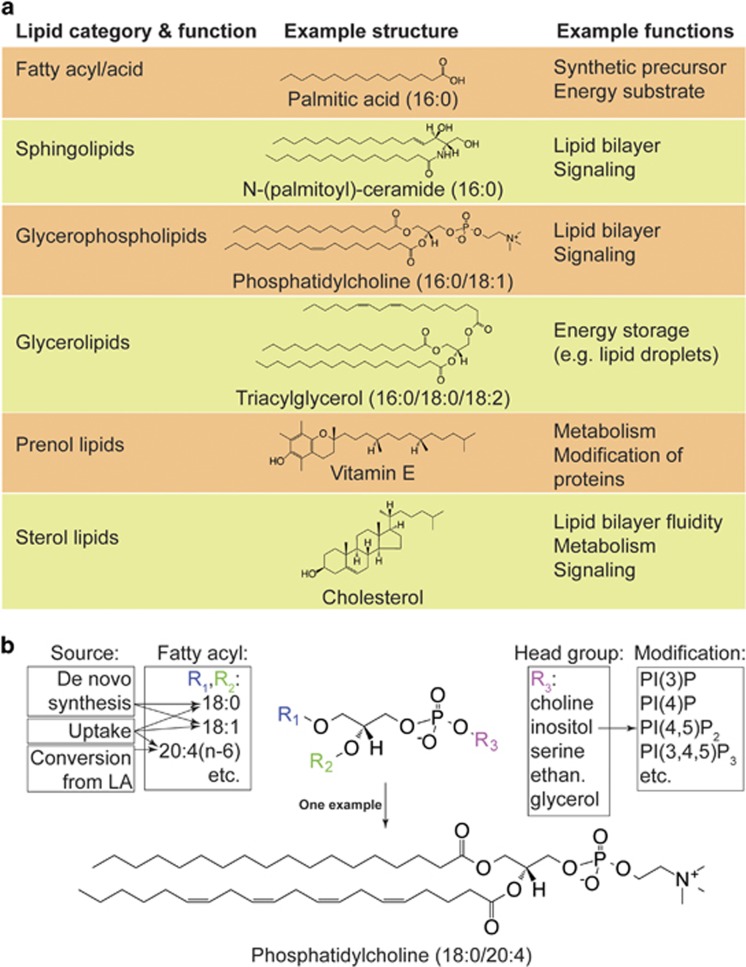
Figure 1.
Overview of lipids and lipid diversity. (a) Six categories of lipids important for mammalian cell function (see also lipidmaps.org for more information). (b) An example of structural diversity in the glycerophospholipid class. Glycerophospholipids can be esterified at two positions (R1 and R2, respectively) with distinct FAs. SFAs and MUFAs can be synthesized de novo or taken up from the environment. PUFAs are taken up from the environment or synthesized from essential PUFA precursors like linoleic acid (LA, 18:2n-6). The head group conjugated to the phosphate can be one of the several molecules (ethan.: ethanolamine). Inositol can be further modified by phosphorylation, generating additional diversity. The example molecule shows a PC conjugated to an SFA, stearic acid (R1=18:0), and a PUFA, arachidonic acid (R2=20:4n-6)