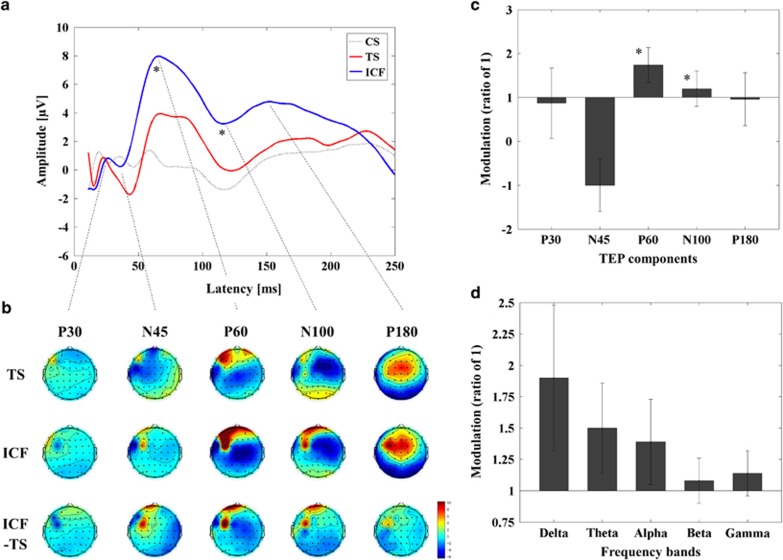
Figure 4.
Facilitatory influence of ICF on TEPs with TMS over DLPFC. (a) Group averaged TEPs following TS (red; delivered at a time equal to 0 ms), ICF (CS.TS) (blue) and CS alone (dotted line; delivered at -10 ms, ie, 10 ms prior to TS). P60 was significantly increased in amplitude similar to M1–ICF, whereas P30 was not evident in DLPFC. In addition, there was a longer lasting increase in EEG-positive potential with a modulation of N100 amplitude. (b) The topographical distribution of TEP components, and their modulation by ICF, is displayed. Note that the topographical distributions of TEPs from TS for DLPFC–ICF and DLPFC–SICI are equivalent, but that the scaling has been adjusted in each case to better visualize the respective changes. (c) The modulation of TEP components by ICF (mean±SEM) is displayed as a ratio of 1 (1 is equivalent to no change relative to the TEP amplitude of TS alone; *P<0.05). Note that DLPFC–ICF increases the positivity of N45 (consistent with M1–ICF), but that this is equivalent to a decrease the amplitude of N45 in DLPFC–ICF, resulting in a negative ratio. (d) DLPFC–ICF did not modulate power in any frequency band. A full color version of this figure is available at the Neuropsychopharmacology journal online.