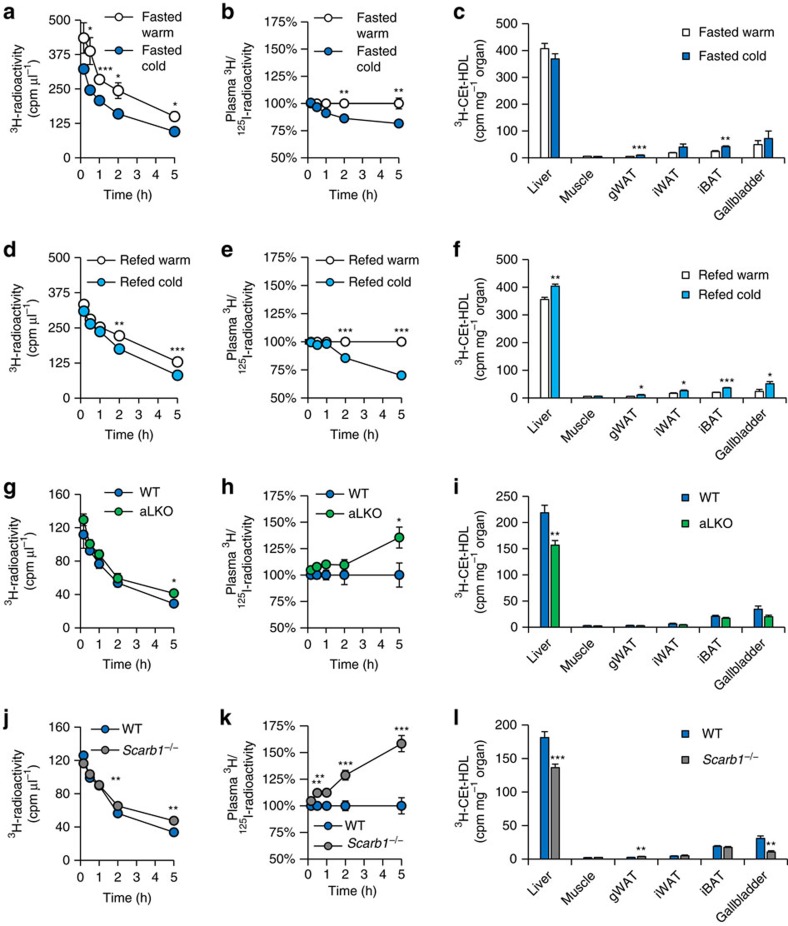
Figure 6. Lipolysis by LPL and hepatic SR-BI increase cold-induced HDL turnover.
125I-protein shell- and 3H-cholesteryl oleoyl ether (CEt) core-radiolabelled HDL were injected into (a–c) fasted and (d–f) re-fed C57BL/6J mice, which had been either cold-exposed for 7 days (cold) or kept under thermoneutral conditions (warm). Double-labelled HDL were also injected into fasted mice cold-adapted for 7 days with (g–i) adipocyte-specific LPL knockout (aLKO) and (j–l) Scarb1−/− mice and wild-type (WT) controls. HDL-derived 3H-CEt clearance from plasma was analysed at indicated time points by determining (a,d,g,j) total and (b,e,h,k) selective clearance. Values for selective clearance are presented as the ratio of 3H/125I radioactivity and calculated for each time point indicated (an accelerated selective HDL-cholesterol clearance from plasma is indicated by a lower ratio of 3H/125I while impaired plasma clearance leads to higher 3H/125I). (c,f,i,l) The organ uptake of HDL-3H-CEt was measured 5 h after injection of radiolabelled HDL. gWAT, gonadal WAT; iWAT, inguinal WAT; iBAT, interscapular BAT. Values are mean±s.e.m. (n=5-7 per group). *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, versus control (Student's t-test).