Figure 1. SCI-associated upregulation of ribosomal biogenesis.
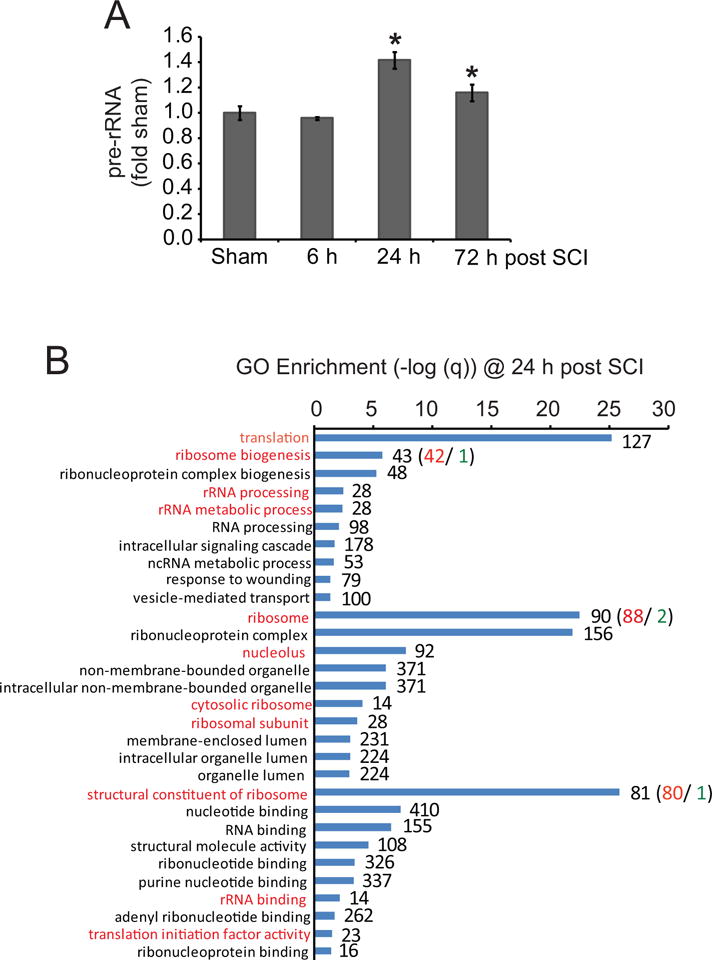
A. Moderate SCI was performed in female mice using IH Impactor, n=4 per group (50 kdyn). Pre-rRNA levels were determined by qRT-PCR with normalization against 18S rRNA. The increases at 24- and 72 h post-injury were significant (u-test, p<0.05, *). Error bars depict SEMs. B. Meta-analysis of microarray data from moderate contusive mouse SCI (T8 level, GEO GSE5296). In the injury epicenter, 2819 significantly affected mRNA transcripts were identified at 24 h (n=3 or 4 for SCI-, and, sham control animals, respectively, p<0.01). Gene ontology terms (GOs) related to translational regulation and ribosomal biogenesis were highly enriched (red-marked GOs). For ribosomal biogenesis-associated GOs, most affected transcripts were upregulated. The graph presents –log (q) values for 10 top enriched GOs from each of the following categories: “biological process”, “cellular component”, and “molecular function”; red or green numbers indicate numbers of upregulated or downregulated mRNAs, respectively. Results of similar analyses for 4 h and 72 h suggest that the ribosomal biogenesis enrichment is specific to 24 h (Fig. S1).
