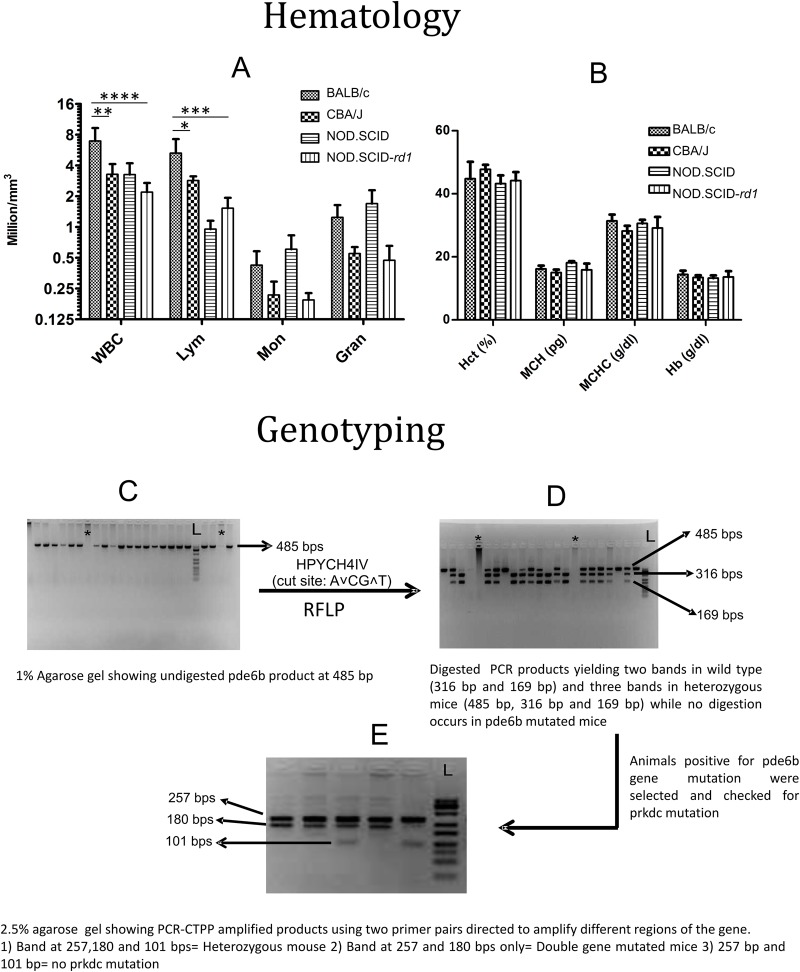
Fig. 1.
Hematological analysis and genotyping for NOD.SCID-rd1 model of RP. (A,B) Graphical representation of comparative analysis for hematological parameters amongst BALB/c, CBA/J and NOD.SCID-rd1 strains of mice (n=8). The result indicates that WBC and lymphocyte proportion of CBA/J and NOD.SCID-rd1 mice is reduced compared to BALB/c; however, there is a drastic reduction in WBC and lymphocyte proportion in NOD.SCID-rd1 mice. Moreover, NOD SCID mice also show an increased monocyte and granulocyte proportion while both CBA/J and NOD.SCID-rd1 exhibit decreased levels of monocytes and granulocytes instead of any elevation. Other parameters like Hct, MCH, MCHC and Hb showed a similar trend in all the strains of mice. (****P<0.0001, ***P≤0.001, **P<0.01and *P≤0.05). (C,D) Gels showing amplified Pde6b product at 485 bp and HPYCH4IV digested Pde6b amplicons respectively. RFLP analysis yields two bands (316 bp and 169 bp) for the wild type, and three bands (485 bp, 316 bp, 169 bp) for heterozygous animals. HypCH4IV, whose cutting site is A∨CG∧T, failed to digest Pde6b mutated amplicons, which undergo single nucleotide mutation in 349th base pair of exon 7. (E) The animals testing positive for Pde6b mutation were further analyzed for Prkdc mutation (which leads to B- and T-cell dysfunction) by PCR-CTPP method. The Prkdc mutated gene amplicons yielded bands at 257 and 180 bp, heterozygous animals at 257 bp, 180 bp and 101 bp, where bands were 257 bp and 101 bp in wild-type animals.