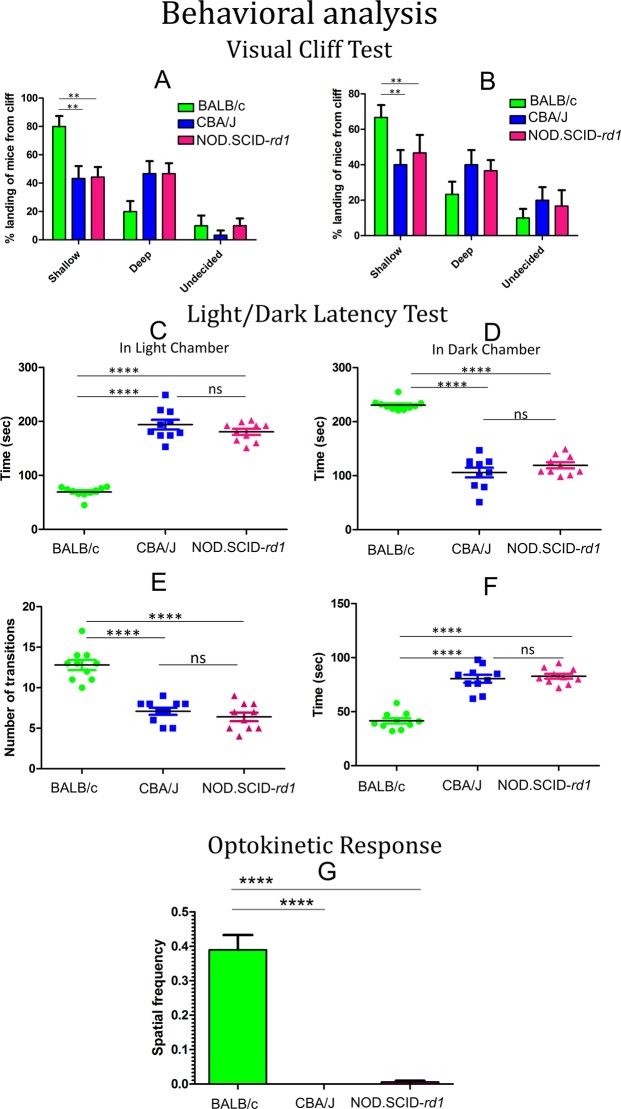
Fig. 6.
Behavioral analysis of NOD.SCID-rd1 model of RP. (A,B) Behavioral analysis (n=10) by visual cliff test in bright (A) as well as dim (B) light showing that BALB/c mice preferred the shallow side of the cliff while both CBA/J and NOD.SCID-rd1 exhibited a 50% tendency to step on either side of the cliff. (C,D) Light/dark latency test analysis indicated non-aversive behavior of CBA/J and NOD.SCID-rd1 towards light that tended to spend more time in light chamber where they were initially placed. However, BALB/c mice were aversive to light and tend to spend more time in dark chamber. (E,F) The exploratory behavior of CBA/J and NOD.SCID-rd1 as indicated by the number of transitions made between both chambers as well as the delay in time taken to enter dark chamber from light chamber, is also reduced compared with BALB/c. (G) The spatial frequency was calculated based on the optokinetic response of mice to various frequencies of gyrating stripes wherein CBA/J and NOD.SCID-rd1 failed to show any response. ****P<0.0001 and **P<0.01.