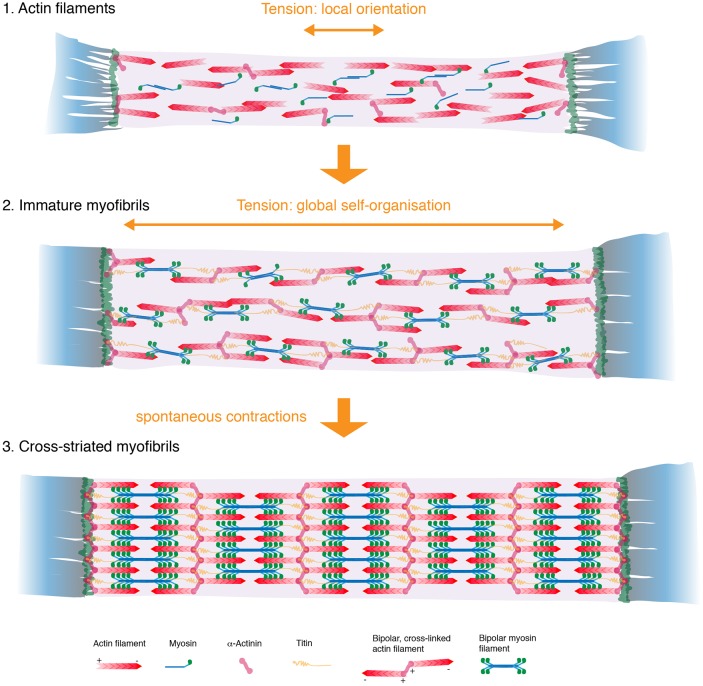
Fig. 8.
Tension-driven model of myofibrillogenesis. Locally, tension orients actin and myosin filaments along the axis of the muscle to assemble linear myofibrils (1). Globally, it coordinates the synchronous formation of periodic actomyosin filaments across the entire muscle fiber (2). Spontaneous muscle twitching contributes to the self-organization of perfectly ordered striated myofibrils (3). For further details, see the Discussion.