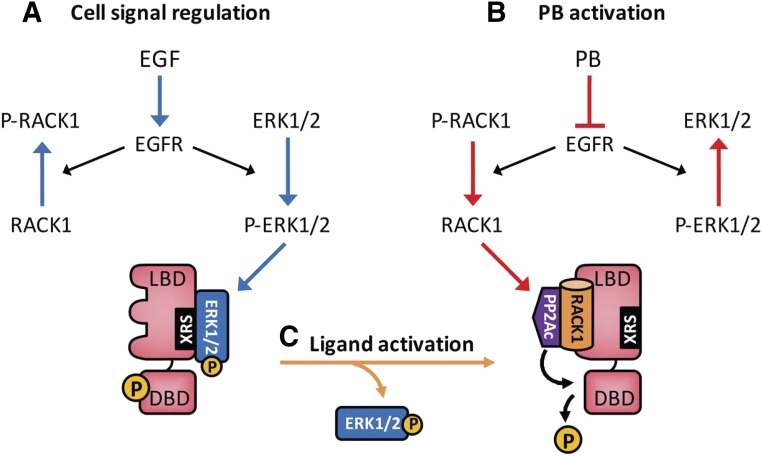
Fig. 1.
The molecular mechanism of PB induction. (A) EGF activates EGFR, preventing CAR from being dephosphorylated and keeping CAR inactivated. (B) PB binds EGFR and represses its signaling, dissociating ERK1/2 from XRS and allowing RACK1/PP2Ac to dephosphorylate threonine 38 for CAR activation. (C) Ligands such as CITCO directly bind phosphorylated CAR, dissociating P-ERK1/2 from XRS. Blue arrows indicate signals to inactivate CAR, and red and orange arrows indicate signals to activate CAR. XRS, xenochemical response signal.