Fig. 1.
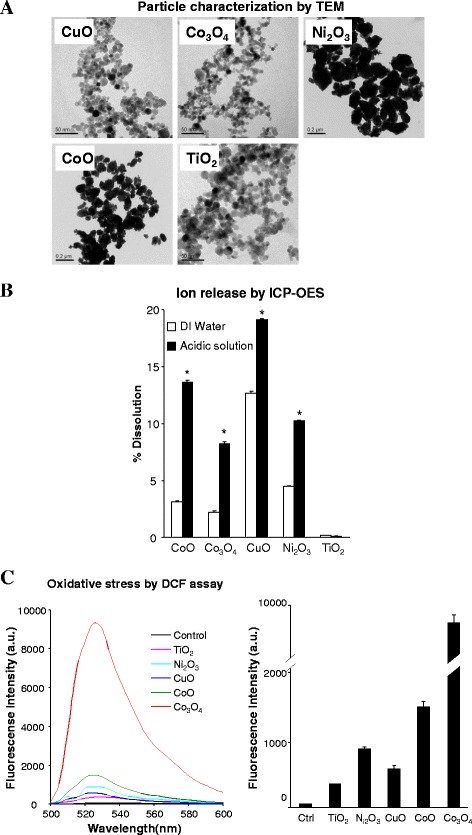
Characterizing the physicochemical properties of MO nanoparticles. a TEM images showing the shape and size of MOx, b Dissolution percentage of MO NPs in DI water and acidic solution, and c Determining the oxidative capability of MOx by DCF assay. The dissolution analysis was performed by suspending 50 μg/mL of each of the nanoparticles in deionized water or acidic solution (pH 4.5, HCl), followed by incubation at room temperature for 24 h. The supernatants were collected by centrifugation at 20000 g for 30 min and digested for ICP-OES measurement. For DCF assay, 200 μg/mL MOx suspensions were incubated with DCF solutions at 25 μg/mL for 2 h. The fluorescence emission spectra of the mixed solutions were collected at 500–600 nm with excitation at 490 nm. * p < 0.05 compared to the ion release in water
