Fig. 1.
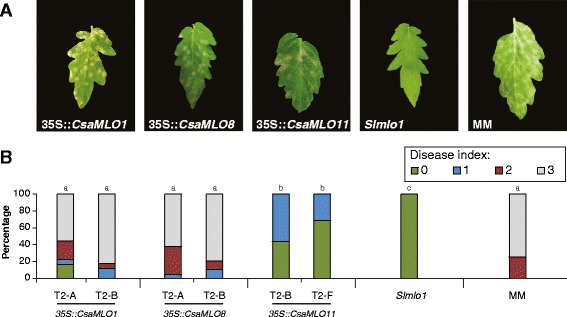
Complementation of a tomato mlo mutant with either CsaMLO1, CsaMLO8 or CsaMLO11. The tomato mlo mutant, with a frameshift deletion in the SlMLO1 gene [11], was transformed with either a 35S::CsaMLO1 construct, a 35S::CsaMLO8 construct or a 35S::CsaMLO11 construct (Table 1). Two individual transformants per transgene were self-pollinated to obtain T2 populations. T2 plants were screened for the presence of the overexpression construct. Plants carrying an overexpression construct were inoculated with O. neolycopersici. a Representative individuals from T2 families expressing either CsaMLO1, CsaMLO8 or CsaMLO11 in the tomato mlo mutant, showing powdery mildew (PM) symptoms. Non-transformed tomato slmlo1 mutant (PM resistant) and cv. Moneymaker (MM, PM susceptible) are shown as controls. b Disease indices were scored visually on a scale from 0 (completely resistant) to 3 (completely susceptible), as described in [11]. T2 families consisted of 16 to 29 individuals positive for the presence of the overexpression construct. Resistant and susceptible controls consisted of 12 individuals. Bars represent percentages of plants within each disease index class. Different letters above bars indicate significant differences between populations (Kruskal-Wallis test with Stepwise-Stepdown Multiple Comparisons, P < 0.05)
