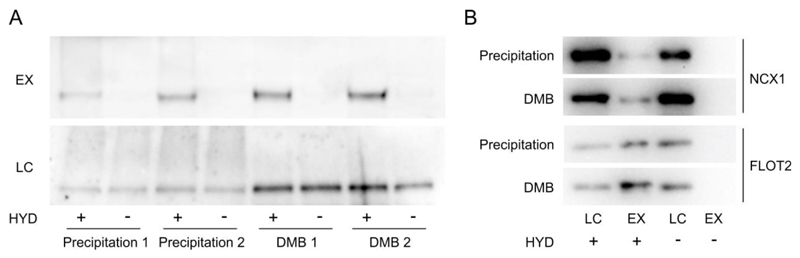
Figure 3.
(A) Use of 2,3-dimethyl-1,3-butadiene in place of precipitation to remove NEM from solution greatly improves detection of FLS2 S-palmitoylation by Acyl-biotin exchange (ABE). The ABE protocol presented in the methods was followed using either chloroform/methanol precipitation or 2,3-dimethyl-1,3-butadiene (DMB) treatment for NEM removal. The same initial extract was split into four and processed in parallel. HYD indicates presence (+) or absence (-) of hydroxylamine required for acyl group cleavage during the biotin labelling step. Samples were bound to neutravidin beads following biotin labelling and enriched proteins were eluted and represent S-palmitoylated proteins (EX). Prior to neutravidin binding a sample was removed as an input loading control (LC). All samples were run on 7.5% SDS-PAGE gels and blotted for FLS2. (B) Use of 2,3-dimethyl-1,3-butadiene in place of precipitation to remove NEM from solution is compatible with acyl -RAC procedures. The acyl-RAC protocol presented in the methods was followed either using acetone precipitation or 2,3-dimethyl-1,3-butadiene treatment for NEM removal. The same initial extract was split into two and processed in parallel. HYD indicates presence (+) or absence (-) of hydroxylamine required for acyl group cleavage during the thiopropyl Sepharose 6b capture step. Thiopropyl Sepharose 6b enriched proteins were eluted and represent S-palmitoylated proteins (EX). Prior to Thiopropyl Sepharose 6b capture a sample was removed as an input loading control (LC).